What does cardiovascular health encompass?
Cardiovascular health describes how well, or how poorly, the heart (“cardio-”) and blood vessels (“-vascular”) move blood throughout the body. Conditions like coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis are commonly associated with cardiovascular health. However, not all cardiovascular diseases have to do with clogged and hardened blood vessels. For example, Raynaud's disease, varicose veins,[1] and congenital heart diseases[2] are also categorized under cardiovascular health. Metrics like heart rate variability and resting heart rate are also linked to cardiovascular health to some degree, but their significance is still being explored.[3][4]
How could diet affect cardiovascular health?
Diet can have major potential effects on cardiovascular health, although the specifics depend on the aspect of health in question. For example, there’s strong evidence to suggest that a diet low in salt and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish[5] like the Mediterranean diet[6] is effective for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and diets high in nitrate-containing foods like beetroot juice, kale, and spinach may have the potential to improve cardiovascular aspects of athletic performance, although the magnitude of these effects for high-performing athletes is questionable.[7]
Which supplements are of most interest for cardiovascular health?
Fish oil has been particularly well studied in the context of cardiovascular health. Several vitamins like folic acid, vitamin D, and vitamin E have also been investigated, as have plant-based supplements like pycnogenol and high-nitrate beetroot juice. Red yeast rice can lower cholesterol, although any supplement with high levels of its active ingredient (lovastatin) cannot be sold legally in the United States. In contrast, some evidence suggests that calcium supplementation may negatively affect cardiovascular health.[8]
Supplement Guide
Examine Database: Cardiovascular Health
Research FeedRead all studies
In this meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, supplementation with garlic improved biomarkers of glycemic control and blood lipids.
Frequently asked questions
Cardiovascular health describes how well, or how poorly, the heart (“cardio-”) and blood vessels (“-vascular”) move blood throughout the body. Conditions like coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis are commonly associated with cardiovascular health. However, not all cardiovascular diseases have to do with clogged and hardened blood vessels. For example, Raynaud's disease, varicose veins,[1] and congenital heart diseases[2] are also categorized under cardiovascular health. Metrics like heart rate variability and resting heart rate are also linked to cardiovascular health to some degree, but their significance is still being explored.[3][4]
Different types of cardiovascular disease (CVD) may benefit most from different amounts, types, or doses of exercise, and major guidelines don’t provide such tailored advice. In 2018, a team of experts created a system called the EXercise Prescription in Everyday practice & Rehabilitative Training (EXPERT) tool to help clinicians give their patients tailored exercise advice based on their needs.
The team released a consensus statement that provides specific exercise recommendations for several cardiovascular risk states based on the evidence they considered.[12] Some of the team’s recommendations are summarized below.
Each recommendation is accompanied by a grade denoting the level of the recommendation.
“A” indicates the recommendation is supported by high-quality systematic reviews or randomized controlled trials that are directly relevant for the population at hand.
“B” indicates high-quality observational evidence or inference from randomized trials supports the recommendation.
“C” indicates the recommendation is supported by well-conducted case-control or cohort studies with overall consistent results that could be applicable to the target population.
“D” indicates the recommendation is supported by poorer-quality observational evidence, inference from higher-quality observational evidence, or expert opinion.
Exercise recommendations by CVD risk factors

Reference: Hansen et al. Sports Med. 2018.[12]
Diet can have major potential effects on cardiovascular health, although the specifics depend on the aspect of health in question. For example, there’s strong evidence to suggest that a diet low in salt and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish[5] like the Mediterranean diet[6] is effective for the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and diets high in nitrate-containing foods like beetroot juice, kale, and spinach may have the potential to improve cardiovascular aspects of athletic performance, although the magnitude of these effects for high-performing athletes is questionable.[7]
In healthy adults, caffeine intake of up to 400 mg per day has not been linked to increases in cardiovascular disease risk.[9][10] However, the evidence is uncertain regarding the long-term effects of regular caffeine intake for people with high blood pressure or pre-existing heart conditions.[9][11] This also applies to people for whom stimulants in general are not recommended. Low to moderate intake may be generally safe, but this must be assessed on a case-by-case basis in consultation with a physician.
Compared to carbs and unsaturated fat, saturated fat has been linked to an increase in some risk factors for heart disease. However, by focusing on a nutrient in isolation, we risk missing the bigger picture: what matters most is your overall diet and lifestyle.
The fat you eat (and the fat you store in your body) is made up of different types of fatty acids, each with a long chain of carbon atoms bonded together. Saturated fatty acids (SFAs) have no double bonds, whereas monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) have one and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have two or more. The “kinks” those bonds form in fatty acid chains prevent the fatty acids from packing close together, which is why unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature, whereas saturated fats usually aren’t (they’re packed solid).
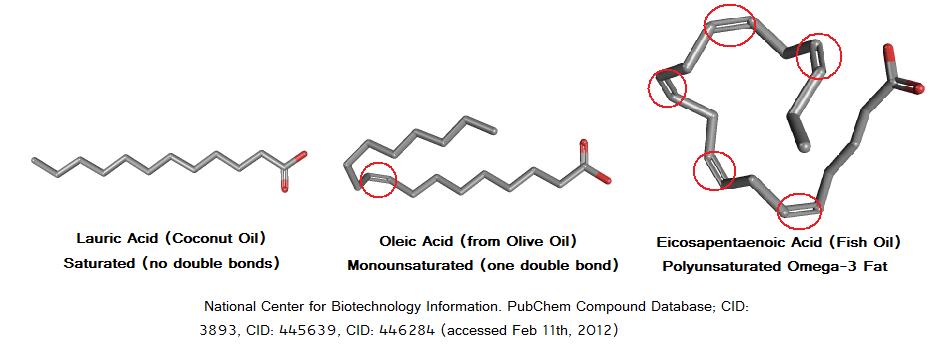
Saturated fats are fatty acids with no double bonds, which is why they are usually solid at room temperature.
However, classifying fatty acids by degree of saturation does not predict how they are handled by the body.[13] Based on the length of its tail (the number of carbons in its chain), a saturated fat belongs to one of four main subcategories, each with its own biological effects.

Even within each subcategory, the various fatty acids have different health effects.
For example, although palmitic acid and stearic acid are both long-chain saturated fats, the former causes a greater increase in blood cholesterol levels.[14] Similarly, although caprylic acid and capric acid are both medium-chain saturated fats, the former results in a larger blood ketone response.[15]
Those variations greatly limit our ability to discuss saturated fat in general. Just as it would be inappropriate to generalize the effects of poisonous mushrooms to all mushrooms, it is inappropriate to generalize the effects of one kind of saturated fat to all kinds of saturated fat.
Saturated fats differ by their length (as indicated by the number of carbons in the fatty acid chain) and can each have unique biological effects.
Medium-chain triglycerides, aka MCTs
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are saturated fats containing 6–10 carbons. Long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) are saturated fats containing 12–18 carbons.
The ketogenic nature of MCTs has led to a growing interest in their use as a food supplement. Traditionally, they’ve served to mimic a ketogenic diet (a very restrictive, very-low-carbohydrate diet) in children with epilepsy.[16] Today, MCTs are also advertised as helping with fat loss, exercise performance, and brain health, though the evidence is limited.
The richest natural source of MCTs, coconut oil, is ≈14% MCTs by weight,[17] so you’d need to eat 100 grams of fat (900 kcal) from coconut oil to consume 14 grams (1 tablespoon) of MCTs. For that reason, people interested in MCTs usually turn to concentrated MCT oils.
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) and long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) are two groups of saturated fats. Your body metabolizes MCTs and LCTs very differently. Unlike LCTs, MCTs are not easily obtained in large quantities from whole foods (the best source is coconut oil, but you would need to eat 7 tablespoons to obtain 1 tablespoonful of MCTs), so they won’t be considered throughout this article.
Why do people think saturated fat is so unhealthy?
A quick history lesson on why people think saturated fat is unhealthy.
Since the 1950s, many studies have linked the consumption of saturated fat with increases in blood cholesterol levels.[18] Those studies, combined with observational research on the association between diet and heart disease,[19] led Dr. Ancel Keys to propose the diet-heart hypothesis, which suggests that saturated fat raises blood cholesterol levels and thus increases the risk of heart disease.[20][21]

Despite some researchers arguing that there were significant flaws in the data Keys used to support his claims,[22] the diet-heart hypothesis persisted and resulted in the belief that a heart-healthy diet should limit saturated fat. Within the academic and medical communities, this conclusion was widely accepted as fact, and it influences official dietary guidelines even today.
Research conducted throughout the later half of the 1900s led Dr. Ancel Keys to propose the diet-heart hypothesis, which posits that dietary saturated fat raises blood cholesterol levels and thus increases the risk of heart disease.
Saturated fat and your heart
Since the diet-heart hypothesis led to official recommendations against saturated-fat intake, it makes sense to address heart disease first.
How does arterial plaque form?
Our arteries are lined with a layer of cells called the endothelium, which functions as a selectively permeable barrier between our blood and the rest of our body. This is akin to our intestinal tract, which allows for the absorption of some nutrients but not others. In our blood, one of the “nutrients” that penetrates the endothelium is low-density lipoprotein (LDL), whose primary job is to transport cholesterol throughout the body.
The key event for the formation of plaques in arteries is the retention of LDL particles in the space beneath the endothelium (called the intima).[23] Once there, LDL is more susceptible to becoming oxidized, which signals the immune system to attack because oxidized LDL is seen as harmful to the body. This inflammatory response involves certain white blood cells called macrophages that literally “eat” the oxidized LDL particles. The LDL-engulfing process turns macrophages into foam cells, which can’t function properly and accumulate into the fatty build-up we call plaque.

As you can see, several events need to occur for heart disease to develop. This helps explain why heart disease has numerous environmental and genetic risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, smoking, lack of exercise, and infection.[24]
Any process that affects LDL retention and oxidation or inflammation is going to influence plaque formation and the risk of suffering from heart disease. Therefore, it makes sense to look at how saturated fat affects each of these processes.
Heart disease is most commonly the result of atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in arteries). Atherosclerosis happens when LDL particles penetrate arterial walls, become oxidized, and are attacked by white blood cells.
Effects of saturated fat on blood lipids
Saturated fat’s effects on blood lipids were thoroughly investigated in a systematic review and meta-analysis published by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2016.[25] This meta-analysis included 84 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving a total of 2,353 healthy adults; it evaluated the effects of replacing 1% of caloric intake from carbohydrates or unsaturated fats with 1% of caloric intake from saturated fat.
To be included in the analysis, all studies were required to meet stringent criteria, so as to best isolate the effects of dietary substitution. For example, all food was provided to the participants, calories and protein were matched between diets, and all interventions lasted at least two weeks. The results are summarized in the table below.

Eating saturated fat instead of unsaturated fat or carbohydrates consistently increased lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in the blood. The one exception was a reduction in triglycerides when saturated fat was consumed instead of carbohydrates. Importantly, these effects were found to be consistent between sexes and across a wide range of baseline blood-lipid values and saturated-fat intakes (1.6–24.4% of calories). They were also consistent between studies, whatever the year of publication.
An important limitation of this meta-analysis is that it could not differentiate between the various food sources of the nutrients, which is an important consideration we shall discuss later. Moreover, studies investigating hydrogenated oils, fish oils, and medium-chain triglycerides were excluded.
Saturated fat increases lipid and lipoprotein concentrations in the blood when compared to carbohydrates, monounsaturated fat, and polyunsaturated fat.
LDL and HDL
Compared to carbohydrates and unsaturated fats, saturated fat raises the levels of lipoproteins and most blood lipids. These changes have well-researched implications for the risk of developing heart disease.
The greater the number of LDL particles in the blood (LDL-P), the more likely some will pass into artery walls, become oxidized, and kickstart plaque formation.[23] Therefore, to predict heart disease, LDL-P matters more than LDL-C,[26][27] which is simply a measure of the amount of cholesterol being carried by LDL particles.
If two people have the same LDL-C but one has cholesterol-rich LDL (large, “fluffy” particles) and the other cholesterol-poor LDL (smaller, denser particles), the second will have a greater LDL-P (more LDL particles total) and be at greater risk of heart disease.
The WHO meta-analysis didn’t cover LDL-P.[25] However, it did report the levels of apolipoprotein B (apoB), the protein component of LDL. Since each LDL particle has one molecule of apoB, apoB concentrations provide a good estimate of LDL-P concentrations and are a strong predictor of heart disease risk.[28][29]
To predict heart disease, LDL-P (the number of LDL particles) matters more than LDL-C (the amount of cholesterol those particles carry). There is one molecule of apolipoprotein B (apoB) in each LDL particle, so apoB is a good estimate of LDL-P. Consuming saturated fat (instead of unsaturated fat) increases apoB concentrations — and therefore your heart-disease risk.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) removes cholesterol from arteries and plaques, protects the endothelium from damage, and inhibits LDL oxidation.[30]
HDL basically does the opposite of LDL. While calling HDL-C “good cholesterol” and LDL-C “bad cholesterol” is simplistic, studies do show that a higher ratio of LDL-C to HDL-C (and of total cholesterol to HDL-C) leads to a higher risk of heart disease. Those ratios matter more than your absolute numbers for LDL-C, HDL-C, and even total cholesterol.[31]
The WHO meta-analysis reported that eating more saturated fat increased HDL-C, but the increase was one-tenth that of LDL-C. Therefore, the ratio of LDL-C to HDL-C (and of total cholesterol to HDL-C) increased,[25] and with it the risk of heart disease.
A similar pattern was seen with apoA1, the major protein component of HDL particles, akin to apoB for LDL particles. Although replacing unsaturated fat by saturated fat led to increases in apoA1, the increase was only 30–60% that in apoB.[25] The ratio of apoB to apoA1 is considered a better predictor of heart-disease risk than other blood lipid biomarkers and their ratios.[32][33] If apoB increases more than apoA1, then the apoB-to-apoA1 ratio increases, and with it the risk of heart disease.
The HDL-C and apoA1 numbers reflect the amount of HDL in the blood. HDL has cardioprotective effects, but while eating saturated fat (instead of unsaturated fat) increases both HDL-C and apoA1, it increases LDL-C and apoB even more.
Finally, the triglyceride to HDL-C ratio represents a strong, independent predictor of heart disease when LDL-C levels are below 160 mg/dL,[34] and has similar predictive ability as LDL-C for determining the extent of atherosclerosis in at-risk patients.[35] Having a triglyceride-to-HDL-C ratio above 3.8 is associated with having more small, dense LDL particles, which are especially susceptible to oxidation.[36]
The WHO meta-analysis reported that eating more polyunsaturated fat reduced the ratio, whereas eating more carbohydrates increased it, when saturated-fat intake was reduced.[25] However, the changes were very small and not of clinical significance. A 10% reduction in calories from saturated fat would increase the triglyceride-to-HDL-C ratio by a mere 0.16 if more carbohydrates were eaten, and decrease it by only 0.04 if more polyunsaturated fat were eaten.
The triglyceride-to-HDL-C ratio correlates with the number of small, dense LDL particles and represents a strong risk factor for heart disease. However, changes in saturated-fat intake have little effect on this ratio.
Effects of saturated fat on inflammation
Plaque development requires that the immune system attack oxidized LDL particles within the arteries. Therefore, reducing systemic inflammation could help fight atherosclerosis, and in this manner decrease the risk of heart disease.[37][38]
Saturated fat may worsen systemic inflammation by increasing the absorption of lipopolysaccharides (LPS),[39] which are bacterial endotoxins that strongly stimulate our immune system.[40][41] Even very small serum concentrations of LPS, on a picogram scale, have the potential to elicit in humans an inflammatory response with a clear dose-response relationship.[42]
However, a systematic review found no consistent associations between consumption of saturated fat and a variety of inflammatory biomarkers, including cytokines, adipokines, acute-phase reactants, and cell adhesion molecules.[43] Clearly, the role of saturated fat on inflammation is not straightforward.
Still, one RCT reported that, compared to a diet high in SFAs, a diet high in MUFAs decreased LDL oxidation, a diet high in omega-6 (n-6) PUFAs increased it, and a diet high in omega-3 (n-3) PUFAs did not affect it.[44] The study authors attributed those differences to the fatty-acid composition of the LDL particles (i.e., to whether they contained mostly SFAs, MUFAs, or either kind of PUFAs).
Saturated fat may raise endotoxin levels to a greater extent than unsaturated fat, but it does not appear to affect systemic inflammation. Omega-6 polyunsaturated fat appears to increase LDL oxidation more than saturated fat (which is bad), whereas monounsaturated fat significantly reduces it (which is good).
Effects of saturated fat on heart disease
Up to this point, we have reviewed the effects of saturated fat on heart-disease risk factors rather than on heart disease itself.
The step between the two should be a small one, but that’s where things turn weird: despite a logical theoretical framework connecting diets high in saturated fat to atherosclerosis, meta-analyses of observational studies haven't reported consistently strong associations between saturated fat intake and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, or cardiovascular disease in general.[45][46]
Even long-term RTCs that assessed hard endpoints of heart disease (such as suffering a heart attack, or dying from one) reported inconsistent links with saturated-fat intake. For instance, one meta-analysis reported that every 5% reduction in calories from SFAs (replaced by PUFAs) reduced the risk of heart disease by ≈10%,[47] but another reported that replacing SFAs by PUFAs was protective only when the PUFAs included both n-3 and n-6 fatty acids — replacing SFAs by only n-6 PUFAs tended to increase the risk of heart disease.[48]
One reason for the discrepancies is the failure of many studies to isolate the effects of altering saturated-fat intake. For example, some studies gave dietary advice to only one of the intervention groups — advice such as eating more plant-based foods; eating more n-3 PUFAs from fish and seafood; eating less sugar; and eating less trans-fat from margarines, shortenings, and partially hydrogenated oils.[49] When looking only at trials that minimized confounding factors, we see that replacing SFAs with primarily n-6 PUFAs has no effect on the risk of developing heart disease or dying from it.[49]
Neither observational studies nor RCTs support the notion that eating a diet high in saturated fat strongly increases the risk of developing heart disease or dying from it.
Understanding the difference between heart-disease risk factors and actual rates of heart disease
So, what gives? We have evidence that eating more saturated fat (instead of unsaturated fat) increases known risk factors for heart disease, such as blood lipids, but studies looking at the big picture do not find a link between saturated fat and heart disease. How can this be?
The simple answer is that fat intake is but a single piece of the heart-disease puzzle. Eating more saturated fat may increase your risk of developing heart disease, but that doesn’t mean you will develop heart disease. Conversely, banning all saturated fat from your diet does not make your heart attack proof.
In other words, rather than singling out any food or nutrient, we need to consider a person’s overall diet and lifestyle.
Let us use dairy as an example.
Dairy fat is ≈70% saturated fat,[50] making it a prime target for nutritional interventions. However, results from observational and experimental studies on the effects of dairy products on blood lipid levels are not conclusive,[51][52] and can even appear contradictory. For instance, there is RCT evidence that diets high in saturated fat from butter increase LDL-C, but that diets equally high in saturated fat from cheese might not.[51] Different dairy products, such as butter and cheese, have different food matrices (structures in which the food compounds are arranged), and thus different metabolic effects.[53]
Similarly, one meta-analysis reported a lack of significant associations between heart disease mortality and high intakes of meat or dairy products (including milk and cheese). [54] However, high intakes of processed meat did increase the risk of heart disease. It is well established that processed meats contain several carcinogenic compounds, which can influence heart disease risk.[55]
Whether saturated fat is good or bad for your heart may depend on what it is replacing — or being replaced by — in your diet. For example, replacing saturated fat by carbohydrates from whole grains is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, whereas replacing saturated fat by carbohydrates from refined grains fails to confer the same benefit.[56] Similarly, replacing SFAs by plant-based MUFAs is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, whereas replacing SFAs by animal-based MUFAs is not.[57]
If you care about your heart, you can’t just focus on saturated fat — or on any other nutrient. You need to look at the foods that provide it, and beyond that, at your overall diet and lifestyle. Doing otherwise means missing the forest for the trees.
Saturated fat and your brain
Studies in animal models and test tubes generally support the position that, compared to diets high in MUFAs or n-3 PUFAs, diets high in SFAs (and, to a lesser extent, diets high in n-6 PUFAs) have detrimental effects on brain development and cognitive function.[58][59] However, whether results in animals can be applied to humans is questionable.
Unfortunately, human studies are scarce. One study reported that eating a diet high in SFAs (from palm oil) increased self-reported anger (4.7 vs. 2.2 out of 5 points) and overall mood disturbances (13 vs. 7 out of 20 points) compared to eating a diet high in MUFAs (from hazelnut oil).[60] Other studies have reported that eating SFAs alters brain activation during cognitive tests and at rest, although the implications of these findings are not known.[61][62]
Studies in animals suggest that diets high in saturated fat may impair cognitive function and brain development. However, studies in humans are few and inconclusive.
Saturated fat and your weight
Appetite
Weight gain or loss depends greatly on caloric intake. According to a review of 24 studies, different types of fat affect subjective appetite similarly, at least in the short-term (e.g., single-meal assessments), in spite of satiety hormones being affected more by saturated than unsaturated fat.[63] However, differences in study protocols and participants make it difficult to draw overarching conclusions.
The effects of fat type on appetite regulation are not clear, but compared to monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, saturated fat appears to be either equally filling or slightly less filling.
Thermogenesis
Compared to meals high in unsaturated fat, meals high in saturated fat tend to result in lower levels of post-meal energy expenditure and fatty-acid oxidation.[64] Studies using isotope tracers indicate that the body would rather use unsaturated than saturated fats as an energy source.[65][66] However, long-term studies are inconsistent.[64]
Compared to unsaturated fat, saturated fat reduces energy expenditure and fat oxidation, but the long-term implications are not clear.
Activity
Eating more monounsaturated fat in place of saturated fat appears to spontaneously increase physical activity levels.[60]
Compared to unsaturated fat, saturated fat might reduce energy expenditure via reductions in physical activity.
Saturated fat and your hormones
Testosterone
Several RCTs have been conducted to evaluate the effects of dietary fat (amount and type) on men’s testosterone levels. To best understand these studies, we must first briefly discuss what they measured.
- Tightly bound testosterone. About two-thirds of the testosterone in your blood is bound to sex-hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). Your body can’t use it.
- Loosely bound testosterone. About a third of the testosterone in your blood is bound to albumin. Your body can use it, with some effort.
- Free testosterone. A small percentage of the testosterone in your blood (1–4%, as a rule) just floats around freely. Your body can readily use it.
Together, your loosely bound testosterone and your free testosterone compose your bioavailable testosterone, which has a greater impact on your health than your total testosterone.
Two studies with large sample sizes, controlled diets, and direct measurement of free testosterone reported that, compared to high-fat diets (33–40% of calories), low-fat diets (14–19% of calories) reduced total testosterone levels in healthy men, but did not alter levels of free or bioavailable testosterone.[67][68] Two other studies with smaller sample sizes, less accurate measurement methods, and less dietary control reported reductions in both total and free testosterone levels.[69][70]
Compared to diets high in fat (30–40% of calories), diets low in fat (14–19% of calories) appear to reduce total testosterone levels, but not necessarily free testosterone levels. In all cases, the reductions are fairly small and not clinically significant.
The big picture
Compared to monounsaturated fat (MUFAs) and omega-6 polyunsaturated fat (n-6 PUFAs), saturated fat (SFAs) does increase several risk factors for heart disease. However, compared to n-6 PUFAs only, SFAs also reduce some risk factors. In other words, eating more MUFAs appears to have the most favorable effect on risk factors for heart disease overall, whereas SFAs and n-6 PUFAs are on relatively equal footing.
There is some evidence that, compared to monounsaturated fat, saturated fat might have a negative effect on cognition, appetite, and energy expenditure; but further research is required.
A diet low in fat (14–19% of calories) might reduce total testosterone levels by 10–15% in otherwise healthy men. Total testosterone remains within normal range, however, and the biologically active free testosterone appears unaffected. Clinical significance is not known.
Fish oil has been particularly well studied in the context of cardiovascular health. Several vitamins like folic acid, vitamin D, and vitamin E have also been investigated, as have plant-based supplements like pycnogenol and high-nitrate beetroot juice. Red yeast rice can lower cholesterol, although any supplement with high levels of its active ingredient (lovastatin) cannot be sold legally in the United States. In contrast, some evidence suggests that calcium supplementation may negatively affect cardiovascular health.[8]
Research is still scarce, but current evidence suggests that, through their effect on calcium regulation, some forms of vitamin K can help prevent osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin K is poorly understood, both by the general public and among health professionals. It has a wide range of potential benefits, but their nature and extent are still uncertain.
Why is that?
Some vitamins are more popular than others. In the past, a lot of research went into vitamin C, which became a popular supplement. Nowadays, a lot of research goes into vitamin D, whose popularity as a supplement is steadily growing.
By contrast, research on vitamin K is still scarce, having slowly developed over the past two decades. Further, it is scattered, because there exist several forms of vitamin K. Some of those forms are present only in a few foods. Others exist in various foods, but only in minute amounts. Few have been the subject of human trials.
The human trials that do exist, however, are overall promising. In order to understand their value and limitations, first you need to know a few basic facts. So let’s begin:
What is vitamin K?
Of the four fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), vitamin K was discovered last. In 1929, Danish scientist Henrik Dam discovered a compound that played a role in coagulation (blood clotting).[71] When he first published his findings, in a German journal, he called this compound Koagulationsvitamin, which became known as vitamin K.
Today, we know that vitamin K participates in some very important biological processes, notably the carboxylation of calcium-binding proteins (including osteocalcin and matrix GLA protein).[72] In other words, vitamin K helps modify proteins so they can bind calcium ions (Ca2+). Through this mechanism, vitamin K partakes in blood clotting, as Henrik Dam discovered, but also of calcium regulation: it helps ensure that more calcium gets deposited in bones and less in soft tissues, thus strengthening bones and reducing arterial stiffness.
What complicates matters is that each vitamin has different forms, called vitamers, each of which may affect you differently. Vitamin K has natural vitamers, K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone), and synthetic vitamers, the best-known of which is K3 (menadione).
Vitamin K1
K1 is produced in plants, where it is involved in photosynthesis: the greener the plant, the greater its chlorophyll content; the greater its chlorophyll content, the greater its K1 content. When it comes to foods, K1 is especially abundant in green leafy vegetables.
K1 makes for 75–90% of the vitamin K in the Western diet.[73] Unfortunately, K1 is tightly bound to chloroplasts (organelles that contain chlorophyll and conduct photosynthesis), so you could be absorbing very little of what you eat[74] — maybe less than 10%.[75] Since vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin, however, its absorption can be enhanced by the co-ingestion of fat: adding fat to cooked spinach can raise K1 bioavailability from 5% to 13%.[76]
Vitamin K2
Things become more complicated here, because just as there are several forms of vitamin K, there are several forms of vitamin K2. To be more precise, the side chain of K1 always has four isoprenoid units (five-carbon structures), so there is only one form of K1, but the side chain of K2 has n isoprenoid units, so there are n forms of K2, called MK-n.[77][78]
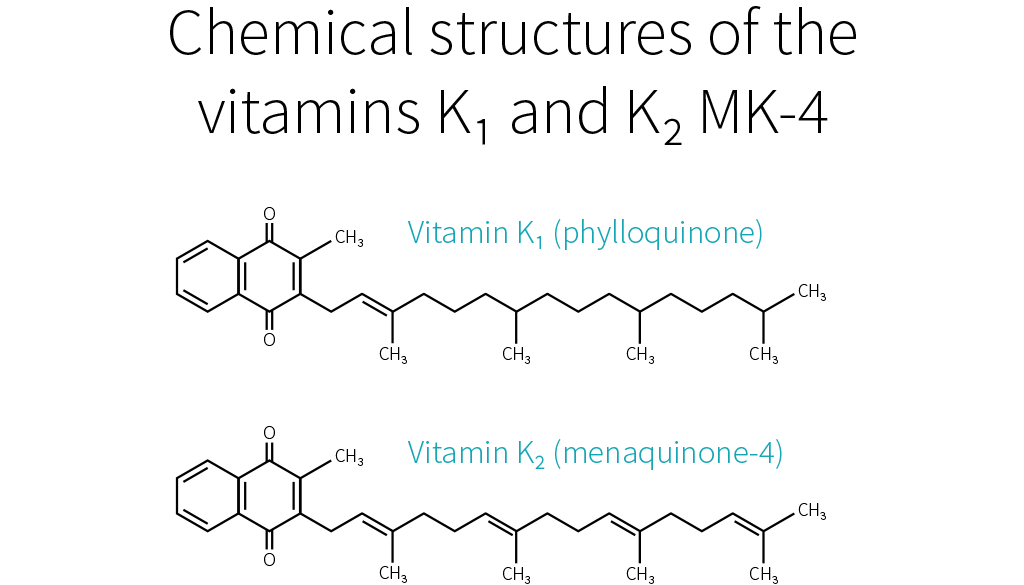
Whereas the side chain of K1 has four saturated isoprenoid units, the side chain of K2 MK-4 has four unsaturated isoprenoid units. Although K1 is directly active in your system, your body can also convert it to MK-4.[79][80][81] How much gets converted depends notably on your genetic heritage.[73]
MK-4 is present in animal products (meat, eggs, and dairy), though only in small quantities. Because those foods usually contain fat, dietary MK-4 should be better absorbed than dietary K1,[82] but future studies will need to confirm this hypothesis.

Other than MK-4, all forms of K2 are produced by bacteria. Your microbiota was once thought to produce three-fourths of the vitamin K you absorb.[83] Vitamin K, however, is mostly produced in the colon, where there are no bile salts to facilitate its absorption, so the actual ratio is probably much lower.[82][84]
Bacteria-produced K2 can be found in fermented foods, such as cheese and curds, but also in liver meat.[85] The richest dietary source of K2 is natto (fermented soybeans), which contains mostly MK-7.[86][87] As it stands, MK-7 is the only form of K2 that can be consumed in supplemental doses through food (i.e., natto). For that reason, MK-7 is the most-studied form of K2, together with MK-4.
K1 and MK-4 both have a side chain composed of four isoprenoid units; their half-life in your blood is 60–90 minutes. MK-7 has a side chain composed of seven isoprenoid units; it remains in your blood for several days. Due to their different side-chain lengths, the various forms tend to be transported on different lipoproteins, which are taken up at different rates by various tissues.[88][89][90][91][92] K1 and MK-4 are used quickly (K1 in the liver, MK-4 in other specific tissues), whereas MK-7 has more time to travel and be used throughout the body (which makes it, in theory, the best option for bone health).
Vitamin K3
K1 and K2 are the only natural forms of vitamin K, but there exist several synthetic forms, the best known of which is K3. However, whereas the natural forms of vitamin K are safe, even in high doses, K3 can interfere with glutathione, your body’s main antioxidant. K3 was once used to treat vitamin K deficiency in infants, but it caused liver toxicity, jaundice, and hemolytic anemia. Nowadays, it is used only in animal feed, in small doses. In the animals, vitamin K3 gets converted into K2 MK-4,[93] which you can consume safely.
Vitamin K is a family of fat-soluble vitamins. K1 and K2, the natural forms, are safe even in high doses. There is only one type of K1; it is found in plants, notably green leafy vegetables; your body can use it directly or convert it to K2 MK-4. Aside from MK-4, all other types of K2 are produced by bacteria, including the bacteria populating your gut. MK-4 is present in animal products (meat, eggs, dairy), whereas other types of K2 can be found in fermented foods and liver meat.
Vitamin K and your health
As far as we know, vitamin K mainly affects bloodclotting, cardiovascular health, and bone health. Epidemiological studies have mostly focused on K1; cardiovascular trials, on K1 and MK-7 (the main type present in natto, the richest dietary source of K2); bone trials, on MK-4 (the type of K2 your body can make out of K1).
Blood clotting
Vitamin K deficiency impairs blood clotting, causing excessive bleeding and bruising. It is rare in adults, but more common in newborns (more than 4 cases per 100,000 births in the UK[94]), where it can result in life-threatening bleeding within the skull. For that reason, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that newborns receive K1 shortly after birth (intramuscular injections have shown greater efficacy than oral administration).[95]
If you suffer from hypercoagulation (if your blood clots too easily), you might be prescribed a vitamin K antagonist (VKA), such as warfarin, a medication that hinders the recycling of vitamin K. Some doctors recommend that VKA users shun vitamin K entirely, but preliminary evidence suggests that, under professional supervision, vitamin K supplements might help stabilize the effects of VKAs.[85]
Which form should be supplemented, though, and in what amount, is still uncertain. There is some evidence that K1 enhances coagulation more than does MK-4[96][97] but less than does MK-7.[90] With regard to daily supplementation, 100 μg of K1 is considered safe, but in some people 10 μg of MK-7 is enough to significantly impair VKA therapy.[98]
Remember that natto is rich in MK-7. A single serving of natto can increase blood clotting for up to four days,[99] so it is one food VKA users should avoid. Other foods should be safe to eat. Please note that in people who do not suffer from hypercoagulation, and thus do not need to medicate with VKA, high intakes of natto have never been correlated to excessive blood clotting. Similarly, human studies saw no increase in blood-clot risk even from 45 mg (45,000 μg) of MK-4 taken once[100] or even thrice[101] daily.
Cardiovascular health
As we saw, vitamin K partakes in calcium regulation: it helps ensure that more calcium gets deposited in bones and less in soft tissues, thus reducing arterial stiffness. This is why people who take vitamin K antagonists, such as warfarin, are more likely to suffer from vascular calcification.[102][103]
Epidemiological studies[104][105][106] and mechanistic evidence[107] suggest that dietary K2 benefits cardiovascular health more than an equal dose of dietary K1.
Clinical trials on supplemental vitamin K have focused on K1[108][109] and MK-7.[110][111][112] Often, those trials used a combination of vitamin D and other nutrients, but with vitamin K being the key difference between the intervention group and the control groups. Both of these forms of vitamin K seem to cause a consistent reduction in arterial stiffness (with better evidence for MK-7), and less consistent reductions in coronary calcification and carotid intima-media thickness. Judging from those trials and the epidemiological evidence, MK-7 seems the better choice.
Bone health
As we have just seen again, vitamin K partakes in calcium regulation: it helps ensure that less calcium gets deposited in soft tissues and more in bones, thus strengthening the latter. This is why people who take vitamin K antagonists, such as warfarin, might be more at risk of bone fractures,[113][114] though not all studies agree they are.[115]
Current evidence suggests that supplementing with vitamin K — or, at least, with certain forms of vitamin K — can benefit bone health, especially in the elderly (who have lower levels of circulating K2).[116] This potential should be explored, since, as the world population grows (and grows older), so does the number of osteoporotic fractures.[117] [118][119]
MK-7 appears to support the carboxylation of osteocalcin (a major calcium-binding protein in bones) more efficiently than K1.[90] Clinical trials suggest that, for the purpose of increasing bone density, MK-4 and MK-7 work more reliably than K1.[120]
More significantly, a meta-analysis of MK-4 trials found an overall decrease in fracture risk.[121] The effect of K1 or MK-7 supplementation on fracture risk is less clear. Only one K1 trial looked at fracture risk; it reported a decrease, but without a concomitant increase in bone mineral density.[122] Of the two MK-7 trials, one reported no difference in the number of fractures between the placebo group and the MK-7 group,[123] whereas the other reported fewer fractures in the MK-7 group;[124] there were, however, no statistical analyses for either study.
More research on vitamin K and fracture risk will be needed to clarify the effects of the different forms at different dosages. Currently, if you wish to supplement for bone health, a very high dose of MK-4 (45,000 μg) is the option best supported by human studies.[121] Those studies, all in Japanese people, focused on the prevention of bone fractures, and yes, much smaller dosages can probably help support bone health; but how much smaller?
In a 12-month study, 20 patients suffering from a chronic kidney disorder were given a daily glucocorticoid (a corticosteroid that has for side effect to decrease bone formation and increase bone resorption). In addition, half the patients received 15 mg of MK-4 daily, while the other half received a placebo. The placebo group experienced bone-density loss (BDL) in the lumbar spine, while the MK-4 group did not.[125]
More recently, a 12-month study in 48 postmenopausal Japanese women gave 1.5 mg of MK-4 daily to half of them and found a significant reduction in forearm BDL, but not in hip BDL, and it didn’t evaluate fractures.[126]
So there is some evidence for dosages lower than 45 mg/day. It is, however, a lot weaker.
In healthy people, vitamin K supplementation does not increase the risk of blood clots. Judging from limited evidence, MK-7 seems to be the best form of vitamin K for cardiovascular health, and MK-4 the best form of vitamin K for bone health.
How much vitamin K do you need?
Since vitamin K is crucial to your health, why is it the subject of relatively few studies? One of the reasons is simply that vitamin K deficiency is very rare in healthy, well-fed adults. It is mostly a concern in newborns, in people who have been prescribed a vitamin K antagonist, in people who suffer from severe liver damage, and in people who have problems absorbing fat.[127][128][129]
Vitamin K is abundant in a balanced diet, and the bacteria in your colon can also produce some. Moreover, your body can recycle it many times, and this vitamin K-epoxide cycle more than makes up for the limited ability your body shows for storing vitamin K.
Still, you can recycle vitamin K many times, but not forever, and so you still need to consume some regularly. But how much, exactly?
No one knows. There is, as yet, not enough evidence to set a Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin K, so an Adequate Intake (AI) has been established at a level assumed to prevent excessive bleeding. In the United States, the AI for vitamin K is 120 μg/day for men and 90 μg/day for women. In Europe, the AI for vitamin K is 70 μg/day for men and women. More recent research, however, suggests that those numbers should be increased.[89]
Since 100 g of collards contain, on average, 360 μg of vitamin K,[130][77] getting enough vitamin K looks easy. But can’t you just as easily get too much?
Fortunately, no. Though allergic reactions have occurred with vitamin K injections,[131][132][133] no incidence of actual toxicity has ever been reported in people taking natural vitamin K, even in high supplemental doses.[134] For that reason, neither the FDA nor the EFSA has set a Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for vitamin K. One should note, however, that we lack long-term, high-dose studies on vitamin K safety.
Sources of vitamin K
K1 can be found in plant products, notably green leafy vegetables. K2 MK-4 can be found in animal products (meat, eggs, and dairy). The other types of K2 can be found in fermented foods and liver meat.

Table references: [135][136][77][137][138][92][130][139][140]
Meats’ vitamin K content correlates positively but non-linearly with their fat content and will vary according to the animal’s diet (and thus country of origin). Forms of K2 other than MK-4 and MK-7 have not been well studied but are likely to have some benefit — cheeses and beef liver are notable sources of others forms of K2[136][140] and cheese consumption is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.[141]
While well-conducted controlled trials provide the most reliable evidence, most such trials used amounts of vitamin K2 that far exceed what could be obtained through foods, save for natto. This leaves us wondering if dietary K2 has any effect.
Fortunately, it seems to be the case: a high dietary intake of K2 (≥33 μg/day seems optimal) may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease — an effect a high dietary intake of K1 doesn’t appear to have.[104][106][105][142] It doesn’t mean, of course, that foods rich in K1 are valueless: dietary K1 intake will protect you from excessive bleeding and is inversely associated with risk of bone fractures.[143]
Observational studies, however, are less reliable than controlled trials, so we know less about the effects of dietary intake than about the effects of supplemental intake. If you wish to supplement with vitamin K, here are the dosages supported by the current evidence:
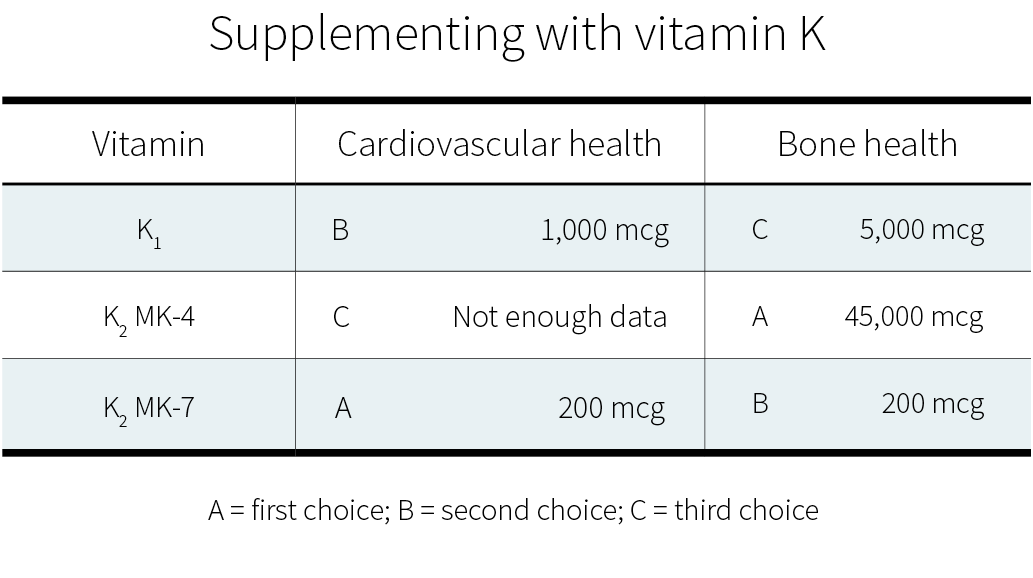
Summary
Although much more research needs to be performed, there is early evidence that vitamin K, whether in food or in supplemental form, can benefit cardiovascular health and bone health.

Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the #1 cause of death globally. But a mix of the right foods and complementary supplements can help decrease your risk factors.
February is National Heart Month. Although heart disease is the leading cause of death for men and women worldwide, it’s largely preventable. That makes heart-health supplements a big business, which means a lot of hype and marketing fluff by various supplement companies.
So we’ve taken it upon ourselves to analyze five supplements that have actual evidence behind their benefits. As always, remember to always consult with your physician before taking anything — some supplements have medication interactions.
Nitrates
Nitrates are one of the reasons why vegetables are so good for you. Nitrates break down into nitrites, which circulate in the body and are turned into nitric oxide (NO). Nitrates, found abundantly in beetroot and a variety of leafy greens (arugula, collards, etc.), are a reliable and effective way to increase nitric oxide synthesis in the body. Elevated NO levels are associated with better circulation and lower blood pressure.[144]
Eating a diet with a good amount of nitrate-containing vegetables decreases your risk for hypertension[144] and can improve endothelial cell function (the cells that line the inside of your blood vessels).[145] As an added bonus, increasing your overall vegetable (and fruit!) intake can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and premature death.[146]
Although you can find nitrates in processed meats, it’s not quite the same as getting them through vegetables. It is thought that various compounds in the meat interact with the nitrates during cooking and processing to form potentially pro-carcinogenic elements like nitrosamines. You can read up on this process and how it may affect your health here: Scientists found that red meat causes cancer ... or did they?
Garlic
While garlic can also enhance NO signaling in the body, its blood pressure lowering effects are mostly due to another compound: hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Whether part of your diet or supplemented, garlic is a cheap and potent way to increase hydrogen sulfide signaling in the body — which in turn relaxes blood vessels and lowers blood pressure.[147]
In those with elevated cholesterol (>200 mg/dL, >5.5 mmol/L), consistently consuming garlic for two months or more can moderately reduce total as well as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and can slightly bump up high-density lipoprotein (HDL).[148] Because it can improve several cardiovascular parameters, garlic makes a good heart-health supplement.
Vitamin K2
A healthy artery is a flexible one. During arterial calcification, calcium adheres to the artery wall, increasing its stiffness. Arterial stiffness and flexibility are very reliable biomarkers of mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Vitamin K2, found in egg yolks and some fermented foods, is one of the few dietary supplements that may be able to reduce arterial calcification[107] and stiffness.[111]
Vitamin K can roughly be broken up into 3 groups: K1, K2, and K3. K1 plays a large role in blood clotting, while K2 is responsible for calcium regulation. K3 is a synthetic provitamin not used in human food fortification or supplementation, as it can harm your health.[134]
While most can get adequate K1 from eating green leafy vegetables, K2 supplementation may be necessary to reap some of K2 cardiovascular benefits.
Bonus: Vitamin K2 provides benefits for bone health too![121] It’s especially useful if you take vitamin D and calcium.
Berberine
Insulin resistance can worsen cardiovascular health over time, since chronically elevated blood sugars can cause tissue damage and increased blood pressure.[149][150]
Berberine is an AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) activator — which means it can help draw glucose and lipids into a cell, allowing them to be used as energy.
With blood sugar reduction comparable to the diabetes drug Metformin, berberine is a very potent blood glucose-lowering agent that can be beneficial for people with impaired glucose regulation. When paired with lifestyle interventions, berberine can greatly improve glucose levels (HbA1c) and help bring down high cholesterol in those with type 2 diabetes.[151]
Taurine
Taurine (L-taurine) is a conditionally essential amino acid found abundantly in the body — particularly in heart tissues where it helps maintain a regular heartbeat.[152] Under healthy conditions, our bodies can produce taurine from the amino acids methionine and cysteine and from vitamin B6.
In patients with heart failure, short-term taurine supplementation (~2 weeks) yielded improvements in cardiovascular function surrounding a bout of exercise.[153][154][155] Studies have also suggested that taurine may have some beneficial effects on blood pressure in those with pre-hypertension or hypertension.[156][157]
Better heart health through food and supplementation
Adding more garlic, leafy greens, and beets to your diet is an easy first step to protect your heart and February is the perfect time to get started!
Remember — supplementation is complimentary to good nutrition, not a replacement for it (and make sure you’re getting high-quality sleep and a fair amount of exercise). It’s not sexy and it’s not a magic pill, but that’s what the evidence points towards.
If you want more specific details on when to take these supplements, how much to take, and step-by-step directions, check out our Heart & Circulation Supplement Guide, a thorough guide on the latest evidence for heart health supplements.
Eggs increasing cholesterol depends on your genetics. They don't seem to increase the risk of heart disease unless you have a poor diet.
Historically, nutrition guidelines for reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) have included recommendations to limit dietary cholesterol. However, the 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans did not issue explicit guidance for dietary cholesterol intake due to inconsistencies in the evidence base. Does this mean eggs can be on the breakfast menu every day without raising CVD risk?
Eggs are a relatively inexpensive and nutrient-dense food. They are a high-quality source of protein and rich in choline, vitamin B2, and the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin.[158] They also contain a notable amount of cholesterol: about 186 mg per large egg.
Evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrates that foods high in cholesterol increase low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C),[159] which increases the risk of CVD.[160] More specifically, it’s reported that the consumption of more than 1 egg per day increases LDL-C by about 7.7 mg/dL (0.2 mmol/L), with similar effects in healthy people and people with dyslipidemia.[161]
Nonetheless, studies report the average response and the individual response to dietary cholesterol is highly variable. It appears that the majority of people are able to roughly maintain LDL-C in response to an increase in dietary cholesterol intake.[162][163][164] This lack of response is due to a combination of suppression in endogenous cholesterol synthesis, a reduction in dietary cholesterol absorption, and an increase in biliary excretion of cholesterol.[165]
On the other hand, there is a notable subset of individuals who, partly due to genetic differences, lack these feedback control mechanisms and experience a significant increase in LDL-C in response to increases in dietary cholesterol intake (i.e., hyper-responders).[166] In this population, it may be particularly worthwhile to limit egg consumption to prevent LDL-C from rising to an unhealthy level.
For many people, moderate egg consumption is permissible and possibly even beneficial as part of an otherwise healthy diet. However, hyper-responders and people with high cholesterol or dyslipidemia may benefit from limiting their egg consumption or removing eggs from the diet altogether, as this can lead to a clinically meaningful decrease in LDL-C.[6]
References
- ^Medline Plus: Vascular Diseases. Accessed 5/30/22
- ^Medline Plus: Heart Diseases. Accessed 5/30/22
- ^Larsson SC, Drca N, Mason AM, Burgess SResting Heart Rate and Cardiovascular Disease.Circ Genom Precis Med.(2019-03)
- ^Souza HCD, Philbois SV, Veiga AC, Aguilar BAHeart Rate Variability and Cardiovascular Fitness: What We Know so Far.Vasc Health Risk Manag.(2021)
- ^Donna K Arnett, Roger S Blumenthal, Michelle A Albert, Andrew B Buroker, Zachary D Goldberger, Ellen J Hahn, Cheryl Dennison Himmelfarb, Amit Khera, Donald Lloyd-Jones, J William McEvoy, Erin D Michos, Michael D Miedema, Daniel Muñoz, Sidney C Smith Jr, Salim S Virani, Kim A Williams Sr, Joseph Yeboah, Boback Ziaeian2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice GuidelinesCirculation.(2019 Sep 10)
- ^Frank L J Visseren, François Mach, Yvo M Smulders, David Carballo, Konstantinos C Koskinas, Maria Bäck, Athanase Benetos, Alessandro Biffi, José-Manuel Boavida, Davide Capodanno, Bernard Cosyns, Carolyn Crawford, Constantinos H Davos, Ileana Desormais, Emanuele Di Angelantonio, Oscar H Franco, Sigrun Halvorsen, F D Richard Hobbs, Monika Hollander, Ewa A Jankowska, Matthias Michal, Simona Sacco, Naveed Sattar, Lale Tokgozoglu, Serena Tonstad, Konstantinos P Tsioufis, Ineke van Dis, Isabelle C van Gelder, Christoph Wanner, Bryan Williams, ESC Scientific Document Group, ESC National Cardiac Societies2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practiceEur Heart J.(2021 Sep 7)
- ^Woessner MN, McIlvenna LC, Ortiz de Zevallos J, Neil CJ, Allen JDDietary nitrate supplementation in cardiovascular health: an ergogenic aid or exercise therapeutic?Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.(2018-02-01)
- ^Seung-Kwon Myung, Hong-Bae Kim, Yong-Jae Lee, Yoon-Jung Choi, Seung-Won OhCalcium Supplements and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical TrialsNutrients.(2021 Jan 26)
- ^Wikoff D, Welsh BT, Henderson R, Brorby GP, Britt J, Myers E, Goldberger J, Lieberman HR, O'Brien C, Peck J, Tenenbein M, Weaver C, Harvey S, Urban J, Doepker CSystematic review of the potential adverse effects of caffeine consumption in healthy adults, pregnant women, adolescents, and childrenFood Chem Toxicol.(2017 Nov)
- ^Poole R, Kennedy OJ, Roderick P, Fallowfield JA, Hayes PC, Parkes JCoffee consumption and health: umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomesBMJ.(2017 Nov 22)
- ^Voskoboinik A, Kalman JM, Kistler PMCaffeine and Arrhythmias: Time to Grind the DataJACC Clin Electrophysiol.(2018 Apr)
- ^Hansen D, Niebauer J, Cornelissen V, Barna O, Neunhäuserer D, Stettler C, Tonoli C, Greco E, Fagard R, Coninx K, Vanhees L, Piepoli MF, Pedretti R, Ruiz GR, Corrà U, Schmid JP, Davos CH, Edelmann F, Abreu A, Rauch B, Ambrosetti M, Braga SS, Beckers P, Bussotti M, Faggiano P, Garcia-Porrero E, Kouidi E, Lamotte M, Reibis R, Spruit MA, Takken T, Vigorito C, Völler H, Doherty P, Dendale PExercise Prescription in Patients with Different Combinations of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Consensus Statement from the EXPERT Working GroupSports Med.(2018 Aug)
- ^Poudyal H, Brown LShould the pharmacological actions of dietary fatty acids in cardiometabolic disorders be classified based on biological or chemical function?Prog Lipid Res.(2015 Jul)
- ^Grundy SMInfluence of stearic acid on cholesterol metabolism relative to other long-chain fatty acidsAm J Clin Nutr.(1994 Dec)
- ^Vandenberghe C, St-Pierre V, Pierotti T, Fortier M, Castellano C, Cunnane STricaprylin alone increases plasma ketone response more than coconut oil or other medium chain triglycerides: an acute crossover study in healthy adultsCurr Dev Nutr.(2017 Mar)
- ^Neal EG, Chaffe H, Schwartz RH, Lawson MS, Edwards N, Fitzsimmons G, Whitney A, Cross JHA randomized trial of classical and medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diets in the treatment of childhood epilepsyEpilepsia.(2009 May)
- ^Orsavova J, Misurcova L, Ambrozova JV, Vicha R, Mlcek JFatty Acids Composition of Vegetable Oils and Its Contribution to Dietary Energy Intake and Dependence of Cardiovascular Mortality on Dietary Intake of Fatty AcidsInt J Mol Sci.(2015 Jun 5)
- ^KEYS A, ANDERSON JT, GRANDE FPrediction of serum-cholesterol responses of man to changes in fats in the dietLancet.(1957 Nov 16)
- ^KEYS A, GRANDE FRole of dietary fat in human nutrition. III. Diet and the epidemiology of coronary heart diseaseAm J Public Health Nations Health.(1957 Dec)
- ^Keys A, Menotti A, Aravanis C, Blackburn H, Djordevic BS, Buzina R, Dontas AS, Fidanza F, Karvonen MJ, Kimura NThe seven countries study: 2,289 deaths in 15 yearsPrev Med.(1984 Mar)
- ^Keys A, Menotti A, Karvonen MJ, Aravanis C, Blackburn H, Buzina R, Djordjevic BS, Dontas AS, Fidanza F, Keys MHThe diet and 15-year death rate in the seven countries studyAm J Epidemiol.(1986 Dec)
- ^Reiser RSaturated fat in the diet and serum cholesterol concentration: a critical examination of the literatureAm J Clin Nutr.(1973 May)
- ^Tabas I, Williams KJ, Borén JSubendothelial lipoprotein retention as the initiating process in atherosclerosis: update and therapeutic implicationsCirculation.(2007 Oct 16)
- ^Lusis AJAtherosclerosisNature.(2000 Sep 14)
- ^World Health OrganizationEffects of saturated fatty acids on serum lipids and lipoproteins: a systematic review and regression analysis(2016)
- ^Allaire J, Vors C, Couture P, Lamarche BLDL particle number and size and cardiovascular risk: anything new under the sun?Curr Opin Lipidol.(2017 Jun)
- ^Otvos JD, Mora S, Shalaurova I, Greenland P, Mackey RH, Goff DC JrClinical implications of discordance between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and particle numberJ Clin Lipidol.(2011 Mar-Apr)
- ^Contois JH, McConnell JP, Sethi AA, Csako G, Devaraj S, Hoefner DM, Warnick GR, AACC Lipoproteins and Vascular Diseases Division Working Group on Best PracticesApolipoprotein B and cardiovascular disease risk: position statement from the AACC Lipoproteins and Vascular Diseases Division Working Group on Best PracticesClin Chem.(2009 Mar)
- ^Sniderman AD, Williams K, Contois JH, Monroe HM, McQueen MJ, de Graaf J, Furberg CDA meta-analysis of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B as markers of cardiovascular riskCirc Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes.(2011 May)
- ^Feig JE, Feig JL, Dangas GDThe role of HDL in plaque stabilization and regression: basic mechanisms and clinical implicationsCoron Artery Dis.(2016 Nov)
- ^Millán J, Pintó X, Muñoz A, Zúñiga M, Rubiés-Prat J, Pallardo LF, Masana L, Mangas A, Hernández-Mijares A, González-Santos P, Ascaso JF, Pedro-Botet JLipoprotein ratios: Physiological significance and clinical usefulness in cardiovascular preventionVasc Health Risk Manag.(2009)
- ^McQueen MJ, Hawken S, Wang X, Ounpuu S, Sniderman A, Probstfield J, Steyn K, Sanderson JE, Hasani M, Volkova E, Kazmi K, Yusuf S, INTERHEART study investigatorsLipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins as risk markers of myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): a case-control studyLancet.(2008 Jul 19)
- ^Walldius G, Jungner I, Aastveit AH, Holme I, Furberg CD, Sniderman ADThe apoB/apoA-I ratio is better than the cholesterol ratios to estimate the balance between plasma proatherogenic and antiatherogenic lipoproteins and to predict coronary riskClin Chem Lab Med.(2004)
- ^da Luz PL, Cesena FH, Favarato D, Cerqueira ESComparison of serum lipid values in patients with coronary artery disease at 70 years of ageAm J Cardiol.(2005 Dec 15)
- ^da Luz PL, Favarato D, Faria-Neto JR Jr, Lemos P, Chagas ACHigh ratio of triglycerides to HDL-cholesterol predicts extensive coronary diseaseClinics (Sao Paulo).(2008 Aug)
- ^Hanak V, Munoz J, Teague J, Stanley A Jr, Bittner VAccuracy of the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio for prediction of the low-density lipoprotein phenotype BAm J Cardiol.(2004 Jul 15)
- ^Golia E, Limongelli G, Natale F, Fimiani F, Maddaloni V, Pariggiano I, Bianchi R, Crisci M, D'Acierno L, Giordano R, Di Palma G, Conte M, Golino P, Russo MG, Calabrò R, Calabrò PInflammation and cardiovascular disease: from pathogenesis to therapeutic targetCurr Atheroscler Rep.(2014 Sep)
- ^Bertrand MJ, Tardif JCInflammation and beyond: new directions and emerging drugs for treating atherosclerosisExpert Opin Emerg Drugs.(2017 Mar)
- ^Fritsche KLThe science of fatty acids and inflammationAdv Nutr.(2015 May 15)
- ^Rietschel ET, Kirikae T, Schade FU, Mamat U, Schmidt G, Loppnow H, Ulmer AJ, Zähringer U, Seydel U, Di Padova FBacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and functionFASEB J.(1994 Feb)
- ^Miller SI, Ernst RK, Bader MWLPS, TLR4 and infectious disease diversityNat Rev Microbiol.(2005 Jan)
- ^Copeland S, Warren HS, Lowry SF, Calvano SE, Remick D, Inflammation and the Host Response to Injury InvestigatorsAcute inflammatory response to endotoxin in mice and humansClin Diagn Lab Immunol.(2005 Jan)
- ^Santos S, Oliveira A, Lopes CSystematic review of saturated fatty acids on inflammation and circulating levels of adipokinesNutr Res.(2013 Sep)
- ^Kratz M, Cullen P, Kannenberg F, Kassner A, Fobker M, Abuja PM, Assmann G, Wahrburg UEffects of dietary fatty acids on the composition and oxidizability of low-density lipoproteinEur J Clin Nutr.(2002 Jan)
- ^Chowdhury R, Warnakula S, Kunutsor S, Crowe F, Ward HA, Johnson L, Franco OH, Butterworth AS, Forouhi NG, Thompson SG, Khaw KT, Mozaffarian D, Danesh J, Di Angelantonio EAssociation of dietary, circulating, and supplement fatty acids with coronary risk: a systematic review and meta-analysisAnn Intern Med.(2014 Mar 18)
- ^Siri-Tarino PW, Sun Q, Hu FB, Krauss RMMeta-analysis of prospective cohort studies evaluating the association of saturated fat with cardiovascular diseaseAm J Clin Nutr.(2010 Mar)
- ^Mozaffarian D, Micha R, Wallace SEffects on coronary heart disease of increasing polyunsaturated fat in place of saturated fat: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialsPLoS Med.(2010 Mar 23)
- ^Ramsden CE, Hibbeln JR, Majchrzak SF, Davis JMn-6 fatty acid-specific and mixed polyunsaturate dietary interventions have different effects on CHD risk: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trialsBr J Nutr.(2010 Dec)
- ^Hamley SThe effect of replacing saturated fat with mostly n-6 polyunsaturated fat on coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trialsNutr J.(2017 May 19)
- ^Månsson HLFatty acids in bovine milk fatFood Nutr Res.(2008)
- ^Huth PJ, Park KMInfluence of dairy product and milk fat consumption on cardiovascular disease risk: a review of the evidenceAdv Nutr.(2012 May 1)
- ^Lovegrove JA, Hobbs DANew perspectives on dairy and cardiovascular healthProc Nutr Soc.(2016 Aug)
- ^Rosqvist F, Smedman A, Lindmark-Månsson H, Paulsson M, Petrus P, Straniero S, Rudling M, Dahlman I, Risérus UPotential role of milk fat globule membrane in modulating plasma lipoproteins, gene expression, and cholesterol metabolism in humans: a randomized studyAm J Clin Nutr.(2015 Jul)
- ^O'Sullivan TA, Hafekost K, Mitrou F, Lawrence DFood sources of saturated fat and the association with mortality: a meta-analysisAm J Public Health.(2013 Sep)
- ^Vlassara H, Cai W, Tripp E, Pyzik R, Yee K, Goldberg L, Tansman L, Chen X, Mani V, Fayad ZA, Nadkarni GN, Striker GE, He JC, Uribarri JOral AGE restriction ameliorates insulin resistance in obese individuals with the metabolic syndrome: a randomised controlled trialDiabetologia.(2016 Oct)
- ^Briggs MA, Petersen KS, Kris-Etherton PMSaturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Replacements for Saturated Fat to Reduce Cardiovascular RiskHealthcare (Basel).(2017 Jun 21)
- ^Zong G, Li Y, Sampson L, Dougherty LW, Willett WC, Wanders AJ, Alssema M, Zock PL, Hu FB, Sun QMonounsaturated fats from plant and animal sources in relation to risk of coronary heart disease among US men and womenThe American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.(2018)
- ^Hussain G, Schmitt F, Loeffler JP, Gonzalez de Aguilar JLFatting the brain: a brief of recent researchFront Cell Neurosci.(2013 Sep 9)
- ^Fernandes MF, Mutch DM, Leri FThe Relationship between Fatty Acids and Different Depression-Related Brain Regions, and Their Potential Role as Biomarkers of Response to AntidepressantsNutrients.(2017 Mar 17)
- ^Kien CL, Bunn JY, Tompkins CL, Dumas JA, Crain KI, Ebenstein DB, Koves TR, Muoio DMSubstituting dietary monounsaturated fat for saturated fat is associated with increased daily physical activity and resting energy expenditure and with changes in moodAm J Clin Nutr.(2013 Apr)
- ^Dumas JA, Bunn JY, Nickerson J, Crain KI, Ebenstein DB, Tarleton EK, Makarewicz J, Poynter ME, Kien CLDietary saturated fat and monounsaturated fat have reversible effects on brain function and the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in young womenMetabolism.(2016 Oct)
- ^Sartorius T, Ketterer C, Kullmann S, Balzer M, Rotermund C, Binder S, Hallschmid M, Machann J, Schick F, Somoza V, Preissl H, Fritsche A, Häring HU, Hennige AMMonounsaturated fatty acids prevent the aversive effects of obesity on locomotion, brain activity, and sleep behaviorDiabetes.(2012 Jul)
- ^Kaviani S, Cooper JAAppetite responses to high-fat meals or diets of varying fatty acid composition: a comprehensive reviewEur J Clin Nutr.(2017 Oct)
- ^Krishnan S, Cooper JAEffect of dietary fatty acid composition on substrate utilization and body weight maintenance in humansEur J Nutr.(2014 Apr)
- ^Jones PJ, Pencharz PB, Clandinin MTWhole body oxidation of dietary fatty acids: implications for energy utilizationAm J Clin Nutr.(1985 Nov)
- ^Schmidt DE, Allred JB, Kien CLFractional oxidation of chylomicron-derived oleate is greater than that of palmitate in healthy adults fed frequent small mealsJ Lipid Res.(1999 Dec)
- ^Dorgan JF, Judd JT, Longcope C, Brown C, Schatzkin A, Clevidence BA, Campbell WS, Nair PP, Franz C, Kahle L, Taylor PREffects of dietary fat and fiber on plasma and urine androgens and estrogens in men: a controlled feeding studyAm J Clin Nutr.(1996 Dec)
- ^Wang C, Catlin DH, Starcevic B, Heber D, Ambler C, Berman N, Lucas G, Leung A, Schramm K, Lee PW, Hull L, Swerdloff RSLow-fat high-fiber diet decreased serum and urine androgens in menJ Clin Endocrinol Metab.(2005 Jun)
- ^Hämäläinen E, Adlercreutz H, Puska P, Pietinen PDiet and serum sex hormones in healthy menJ Steroid Biochem.(1984 Jan)
- ^Raben A, Kiens B, Richter EA, Rasmussen LB, Svenstrup B, Micic S, Bennett PSerum sex hormones and endurance performance after a lacto-ovo vegetarian and a mixed dietMed Sci Sports Exerc.(1992 Nov)
- ^Dam HThe antihaemorrhagic vitamin of the chickBiochem J.(1935 Jun)
- ^Booth SLRoles for vitamin K beyond coagulationAnnu Rev Nutr.(2009)
- ^Shearer MJ, Newman PRecent trends in the metabolism and cell biology of vitamin K with special reference to vitamin K cycling and MK-4 biosynthesisJ Lipid Res.(2014 Mar)
- ^Garber AK, Binkley NC, Krueger DC, Suttie JWComparison of phylloquinone bioavailability from food sources or a supplement in human subjectsJ Nutr.(1999 Jun)
- ^Gijsbers BL, Jie KS, Vermeer CEffect of food composition on vitamin K absorption in human volunteersBr J Nutr.(1996 Aug)
- ^Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti GOral anticoagulant therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice GuidelinesChest.(2012 Feb)
- ^Booth SLVitamin K: food composition and dietary intakesFood Nutr Res.(2012)
- ^Kurosu M, Begari EVitamin K2 in electron transport system: are enzymes involved in vitamin K2 biosynthesis promising drug targets?Molecules.(2010 Mar 10)
- ^Shearer MJ, Newman PMetabolism and cell biology of vitamin KThromb Haemost.(2008 Oct)
- ^Davidson RT, Foley AL, Engelke JA, Suttie JWConversion of dietary phylloquinone to tissue menaquinone-4 in rats is not dependent on gut bacteriaJ Nutr.(1998 Feb)
- ^Ronden JE, Drittij-Reijnders MJ, Vermeer C, Thijssen HHIntestinal flora is not an intermediate in the phylloquinone-menaquinone-4 conversion in the ratBiochim Biophys Acta.(1998 Jan 8)
- ^Beulens JW, Booth SL, van den Heuvel EG, Stoecklin E, Baka A, Vermeer CThe role of menaquinones (vitamin K₂) in human healthBr J Nutr.(2013 Oct)
- ^Miggiano GA, Robilotta LVitamin K-controlled diet: problems and prospectsClin Ter.(2005 Jan-Apr)
- ^Ichihashi T, Takagishi Y, Uchida K, Yamada HColonic absorption of menaquinone-4 and menaquinone-9 in ratsJ Nutr.(1992 Mar)
- ^Holmes MV, Hunt BJ, Shearer MJThe role of dietary vitamin K in the management of oral vitamin K antagonistsBlood Rev.(2012 Jan)
- ^Ikeda Y, Iki M, Morita A, Kajita E, Kagamimori S, Kagawa Y, Yoneshima HIntake of fermented soybeans, natto, is associated with reduced bone loss in postmenopausal women: Japanese Population-Based Osteoporosis (JPOS) StudyJ Nutr.(2006 May)
- ^Katsuyama H, Ideguchi S, Fukunaga M, Saijoh K, Sunami SUsual dietary intake of fermented soybeans (Natto) is associated with bone mineral density in premenopausal womenJ Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).(2002 Jun)
- ^Sato T, Schurgers LJ, Uenishi KComparison of menaquinone-4 and menaquinone-7 bioavailability in healthy womenNutr J.(2012 Nov 12)
- ^Vermeer CVitamin K: the effect on health beyond coagulation - an overviewFood Nutr Res.(2012)
- ^Schurgers LJ, Teunissen KJ, Hamulyák K, Knapen MH, Vik H, Vermeer CVitamin K-containing dietary supplements: comparison of synthetic vitamin K1 and natto-derived menaquinone-7Blood.(2007 Apr 15)
- ^Schurgers LJ, Vermeer CDifferential lipoprotein transport pathways of K-vitamins in healthy subjectsBiochim Biophys Acta.(2002 Feb 15)
- ^Schurgers LJ, Vermeer CDetermination of phylloquinone and menaquinones in food. Effect of food matrix on circulating vitamin K concentrationsHaemostasis.(2000 Nov-Dec)
- ^Nakagawa K, Hirota Y, Sawada N, Yuge N, Watanabe M, Uchino Y, Okuda N, Shimomura Y, Suhara Y, Okano TIdentification of UBIAD1 as a novel human menaquinone-4 biosynthetic enzymeNature.(2010 Nov 4)
- ^Shearer MJVitamin KLancet.(1995 Jan 28)
- ^American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and NewbornControversies concerning vitamin K and the newborn. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Fetus and NewbornPediatrics.(2003 Jul)
- ^Spronk HM, Soute BA, Schurgers LJ, Thijssen HH, De Mey JG, Vermeer CTissue-specific utilization of menaquinone-4 results in the prevention of arterial calcification in warfarin-treated ratsJ Vasc Res.(2003 Nov-Dec)
- ^Groenen-van Dooren MM, Soute BA, Jie KS, Thijssen HH, Vermeer CThe relative effects of phylloquinone and menaquinone-4 on the blood coagulation factor synthesis in vitamin K-deficient ratsBiochem Pharmacol.(1993 Aug 3)
- ^Theuwissen E, Teunissen KJ, Spronk HM, Hamulyák K, Ten Cate H, Shearer MJ, Vermeer C, Schurgers LJEffect of low-dose supplements of menaquinone-7 (vitamin K2 ) on the stability of oral anticoagulant treatment: dose-response relationship in healthy volunteersJ Thromb Haemost.(2013 Jun)
- ^Schurgers LJ, Shearer MJ, Hamulyák K, Stöcklin E, Vermeer CEffect of vitamin K intake on the stability of oral anticoagulant treatment: dose-response relationships in healthy subjectsBlood.(2004 Nov 1)
- ^Ushiroyama T, Ikeda A, Ueki MEffect of continuous combined therapy with vitamin K(2) and vitamin D(3) on bone mineral density and coagulofibrinolysis function in postmenopausal womenMaturitas.(2002 Mar 25)
- ^Asakura H, Myou S, Ontachi Y, Mizutani T, Kato M, Saito M, Morishita E, Yamazaki M, Nakao SVitamin K administration to elderly patients with osteoporosis induces no hemostatic activation, even in those with suspected vitamin K deficiencyOsteoporos Int.(2001 Dec)
- ^Mayer O Jr, Seidlerová J, Bruthans J, Filipovský J, Timoracká K, Vaněk J, Cerná L, Wohlfahrt P, Cífková R, Theuwissen E, Vermeer CDesphospho-uncarboxylated matrix Gla-protein is associated with mortality risk in patients with chronic stable vascular diseaseAtherosclerosis.(2014 Jul)
- ^Chatrou ML, Winckers K, Hackeng TM, Reutelingsperger CP, Schurgers LJVascular calcification: the price to pay for anticoagulation therapy with vitamin K-antagonistsBlood Rev.(2012 Jul)
- ^Gast GC, de Roos NM, Sluijs I, Bots ML, Beulens JW, Geleijnse JM, Witteman JC, Grobbee DE, Peeters PH, van der Schouw YTA high menaquinone intake reduces the incidence of coronary heart diseaseNutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.(2009 Sep)
- ^Beulens JW, Bots ML, Atsma F, Bartelink ML, Prokop M, Geleijnse JM, Witteman JC, Grobbee DE, van der Schouw YTHigh dietary menaquinone intake is associated with reduced coronary calcificationAtherosclerosis.(2009 Apr)
- ^Geleijnse JM, Vermeer C, Grobbee DE, Schurgers LJ, Knapen MH, van der Meer IM, Hofman A, Witteman JCDietary intake of menaquinone is associated with a reduced risk of coronary heart disease: the Rotterdam StudyJ Nutr.(2004 Nov)
- ^El Asmar MS, Naoum JJ, Arbid EJVitamin k dependent proteins and the role of vitamin k2 in the modulation of vascular calcification: a reviewOman Med J.(2014 May)
- ^Shea MK, O'Donnell CJ, Hoffmann U, Dallal GE, Dawson-Hughes B, Ordovas JM, Price PA, Williamson MK, Booth SLVitamin K supplementation and progression of coronary artery calcium in older men and womenAm J Clin Nutr.(2009 Jun)
- ^Braam LA, Hoeks AP, Brouns F, Hamulyák K, Gerichhausen MJ, Vermeer CBeneficial effects of vitamins D and K on the elastic properties of the vessel wall in postmenopausal women: a follow-up studyThromb Haemost.(2004 Feb)
- ^Kurnatowska I, Grzelak P, Masajtis-Zagajewska A, Kaczmarska M, Stefańczyk L, Vermeer C, Maresz K, Nowicki MEffect of vitamin K2 on progression of atherosclerosis and vascular calcification in nondialyzed patients with chronic kidney disease stages 3-5Pol Arch Med Wewn.(2015)
- ^Knapen MH, Braam LA, Drummen NE, Bekers O, Hoeks AP, Vermeer CMenaquinone-7 supplementation improves arterial stiffness in healthy postmenopausal women. A double-blind randomised clinical trialThromb Haemost.(2015 May)
- ^Fulton RL, McMurdo ME, Hill A, Abboud RJ, Arnold GP, Struthers AD, Khan F, Vermeer C, Knapen MH, Drummen NE, Witham MDEffect of Vitamin K on Vascular Health and Physical Function in Older People with Vascular Disease--A Randomised Controlled TrialJ Nutr Health Aging.(2016 Mar)
- ^Caraballo PJ, Heit JA, Atkinson EJ, Silverstein MD, O'Fallon WM, Castro MR, Melton LJ 3rdLong-term use of oral anticoagulants and the risk of fractureArch Intern Med.(1999 Aug 9-23)
- ^Gage BF, Birman-Deych E, Radford MJ, Nilasena DS, Binder EFRisk of osteoporotic fracture in elderly patients taking warfarin: results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation 2Arch Intern Med.(2006 Jan 23)
- ^Jamal SA, Browner WS, Bauer DC, Cummings SRWarfarin use and risk for osteoporosis in elderly women. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research GroupAnn Intern Med.(1998 May 15)
- ^Hodges SJ, Pilkington MJ, Shearer MJ, Bitensky L, Chayen JAge-related changes in the circulating levels of congeners of vitamin K2, menaquinone-7 and menaquinone-8Clin Sci (Lond).(1990 Jan)
- ^Pisani P, Renna MD, Conversano F, Casciaro E, Di Paola M, Quarta E, Muratore M, Casciaro SMajor osteoporotic fragility fractures: Risk factor updates and societal impactWorld J Orthop.(2016 Mar 18)
- ^Dhanwal DK, Dennison EM, Harvey NC, Cooper CEpidemiology of hip fracture: Worldwide geographic variationIndian J Orthop.(2011 Jan)
- ^Johnell O, Kanis JAAn estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fracturesOsteoporos Int.(2006 Dec)
- ^Fang Y, Hu C, Tao X, Wan Y, Tao FEffect of vitamin K on bone mineral density: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialsJ Bone Miner Metab.(2012 Jan)
- ^Cockayne S, Adamson J, Lanham-New S, Shearer MJ, Gilbody S, Torgerson DJVitamin K and the prevention of fractures: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trialsArch Intern Med.(2006 Jun 26)
- ^Cheung AM, Tile L, Lee Y, Tomlinson G, Hawker G, Scher J, Hu H, Vieth R, Thompson L, Jamal S, Josse RVitamin K supplementation in postmenopausal women with osteopenia (ECKO trial): a randomized controlled trialPLoS Med.(2008 Oct 14)
- ^Emaus N, Gjesdal CG, Almås B, Christensen M, Grimsgaard AS, Berntsen GK, Salomonsen L, Fønnebø VVitamin K2 supplementation does not influence bone loss in early menopausal women: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trialOsteoporos Int.(2010 Oct)
- ^Knapen MH, Drummen NE, Smit E, Vermeer C, Theuwissen EThree-year low-dose menaquinone-7 supplementation helps decrease bone loss in healthy postmenopausal womenOsteoporos Int.(2013 Sep)
- ^Sasaki N, Kusano E, Takahashi H, Ando Y, Yano K, Tsuda E, Asano YVitamin K2 inhibits glucocorticoid-induced bone loss partly by preventing the reduction of osteoprotegerin (OPG)J Bone Miner Metab.(2005)
- ^Koitaya N, Sekiguchi M, Tousen Y, Nishide Y, Morita A, Yamauchi J, Gando Y, Miyachi M, Aoki M, Komatsu M, Watanabe F, Morishita K, Ishimi YLow-dose vitamin K2 (MK-4) supplementation for 12 months improves bone metabolism and prevents forearm bone loss in postmenopausal Japanese womenJ Bone Miner Metab.(2013 May 24)
- ^Nowak JK, Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk U, Landowski P, Szaflarska-Poplawska A, Klincewicz B, Adamczak D, Banasiewicz T, Plawski A, Walkowiak JPrevalence and correlates of vitamin K deficiency in children with inflammatory bowel diseaseSci Rep.(2014 Apr 24)
- ^Jagannath VA, Fedorowicz Z, Thaker V, Chang ABVitamin K supplementation for cystic fibrosisCochrane Database Syst Rev.(2013 Apr 30)
- ^Nakajima S, Iijima H, Egawa S, Shinzaki S, Kondo J, Inoue T, Hayashi Y, Ying J, Mukai A, Akasaka T, Nishida T, Kanto T, Tsujii M, Hayashi NAssociation of vitamin K deficiency with bone metabolism and clinical disease activity in inflammatory bowel diseaseNutrition.(2011 Oct)
- ^Booth SL, Pennington JA, Sadowski JAFood sources and dietary intakes of vitamin K-1 (phylloquinone) in the American diet: data from the FDA Total Diet StudyJ Am Diet Assoc.(1996 Feb)
- ^Shiratori T, Sato A, Fukuzawa M, Kondo N, Tanno SSevere Dextran-Induced Anaphylactic Shock during Induction of Hypertension-Hypervolemia-Hemodilution Therapy following Subarachnoid HemorrhageCase Rep Crit Care.(2015)
- ^Riegert-Johnson DL, Volcheck GWThe incidence of anaphylaxis following intravenous phytonadione (vitamin K1): a 5-year retrospective reviewAnn Allergy Asthma Immunol.(2002 Oct)
- ^Bullen AW, Miller JP, Cunliffe WJ, Losowsky MSSkin reactions caused by vitamin K in patients with liver diseaseBr J Dermatol.(1978 May)
- ^Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on MicronutrientsDietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc
- ^Fu X, Shen X, Finnan EG, Haytowitz DB, Booth SLMeasurement of Multiple Vitamin K Forms in Processed and Fresh-Cut Pork Products in the U.S. Food SupplyJ Agric Food Chem.(2016 Jun 8)
- ^Manoury E, Jourdon K, Boyaval P, Fourcassié PQuantitative measurement of vitamin K2 (menaquinones) in various fermented dairy products using a reliable high-performance liquid chromatography methodJ Dairy Sci.(2013 Mar)
- ^Kamao M, Suhara Y, Tsugawa N, Uwano M, Yamaguchi N, Uenishi K, Ishida H, Sasaki S, Okano TVitamin K content of foods and dietary vitamin K intake in Japanese young womenJ Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo).(2007 Dec)
- ^Elder SJ, Haytowitz DB, Howe J, Peterson JW, Booth SLVitamin k contents of meat, dairy, and fast food in the u.s. DietJ Agric Food Chem.(2006 Jan 25)
- ^Shimogawara K, Muto SPurification of Chlamydomonas 28-kDa ubiquitinated protein and its identification as ubiquitinated histone H2BArch Biochem Biophys.(1992 Apr)
- ^Hirauchi K, Sakano T, Notsumoto S, Nagaoka T, Morimoto A, Fujimoto K, Masuda S, Suzuki YMeasurement of K vitamins in animal tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detectionJ Chromatogr.(1989 Dec 29)
- ^Chen GC, Wang Y, Tong X, Szeto IMY, Smit G, Li ZN, Qin LQCheese consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of prospective studiesEur J Nutr.(2017 Dec)
- ^Villines TC, Hatzigeorgiou C, Feuerstein IM, O'Malley PG, Taylor AJVitamin K1 intake and coronary calcificationCoron Artery Dis.(2005 May)
- ^Hao G, Zhang B, Gu M, Chen C, Zhang Q, Zhang G, Cao XVitamin K intake and the risk of fractures: A meta-analysisMedicine (Baltimore).(2017 Apr)
- ^Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kabir A, Azizi F, Ghasemi AThe Nitrate-Independent Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect of Beetroot Juice: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisAdv Nutr.(2017 Nov 15)
- ^Lara J, Ashor AW, Oggioni C, Ahluwalia A, Mathers JC, Siervo MEffects of inorganic nitrate and beetroot supplementation on endothelial function: a systematic review and meta-analysisEur J Nutr.(2016 Mar)
- ^Aune D, Giovannucci E, Boffetta P, Fadnes LT, Keum N, Norat T, Greenwood DC, Riboli E, Vatten LJ, Tonstad SFruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studiesInt J Epidemiol.(2017 Jun 1)
- ^Ried KGarlic Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Individuals, Regulates Serum Cholesterol, and Stimulates Immunity: An Updated Meta-analysis and ReviewJ Nutr.(2016 Feb)
- ^Ried K, Toben C, Fakler PEffect of garlic on serum lipids: an updated meta-analysisNutr Rev.(2013 May)
- ^Kodama S, Saito K, Tanaka S, Horikawa C, Fujiwara K, Hirasawa R, Yachi Y, Sone Y, Tada Iida K, Shimano H, Ohashi Y, Yamada N, Sone HFasting and post-challenge glucose as quantitative cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysisJ Atheroscler Thromb.(2012)
- ^Mannucci E, Dicembrini I, Lauria A, Pozzilli PIs glucose control important for prevention of cardiovascular disease in diabetes?Diabetes Care.(2013 Aug)
- ^Lan J, Zhao Y, Dong F, Yan Z, Zheng W, Fan J, Sun GMeta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertensionJ Ethnopharmacol.(2015 Feb 23)
- ^Schaffer SW, Jong CJ, Ramila KC, Azuma JPhysiological roles of taurine in heart and muscleJ Biomed Sci.(2010 Aug 24)
- ^Ahmadian M, Dabidi Roshan V, Ashourpore ETaurine Supplementation Improves Functional Capacity, Myocardial Oxygen Consumption, and Electrical Activity in Heart FailureJ Diet Suppl.(2017 Jul 4)
- ^Ahmadian M, Roshan VD, Aslani E, Stannard SRTaurine supplementation has anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory effects before and after incremental exercise in heart failureTher Adv Cardiovasc Dis.(2017 Jul)
- ^Beyranvand MR, Khalafi MK, Roshan VD, Choobineh S, Parsa SA, Piranfar MAEffect of taurine supplementation on exercise capacity of patients with heart failureJ Cardiol.(2011 May)
- ^Sun Q, Wang B, Li Y, Sun F, Li P, Xia W, Zhou X, Li Q, Wang X, Chen J, Zeng X, Zhao Z, He H, Liu D, Zhu ZTaurine Supplementation Lowers Blood Pressure and Improves Vascular Function in Prehypertension: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled StudyHypertension.(2016 Mar)
- ^Militante JD, Lombardini JBTreatment of hypertension with oral taurine: experimental and clinical studiesAmino Acids.(2002)
- ^Kuang H, Yang F, Zhang Y, Wang T, Chen GThe Impact of Egg Nutrient Composition and Its Consumption on Cholesterol Homeostasis.Cholesterol.(2018)
- ^Vincent MJ, Allen B, Palacios OM, Haber LT, Maki KCMeta-regression analysis of the effects of dietary cholesterol intake on LDL and HDL cholesterolAm J Clin Nutr.(2019 Jan 1)
- ^Ference BA, Ginsberg HN, Graham I, Ray KK, Packard CJ, Bruckert E, Hegele RA, Krauss RM, Raal FJ, Schunkert H, Watts GF, Borén J, Fazio S, Horton JD, Masana L, Nicholls SJ, Nordestgaard BG, van de Sluis B, Taskinen MR, Tokgözoglu L, Landmesser U, Laufs U, Wiklund O, Stock JK, Chapman MJ, Catapano ALLow-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus PanelEur Heart J.(2017 Aug 21)
- ^Khalighi Sikaroudi M, Soltani S, Kolahdouz-Mohammadi R, Clayton ZS, Fernandez ML, Varse F, Shidfar FThe responses of different dosages of egg consumption on blood lipid profile: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.J Food Biochem.(2020-08)
- ^McNamara DJ, Kolb R, Parker TS, Batwin H, Samuel P, Brown CD, Ahrens EHHeterogeneity of cholesterol homeostasis in man. Response to changes in dietary fat quality and cholesterol quantity.J Clin Invest.(1987-Jun)
- ^Herron KL, Vega-Lopez S, Conde K, Ramjiganesh T, Shachter NS, Fernandez MLMen classified as hypo- or hyperresponders to dietary cholesterol feeding exhibit differences in lipoprotein metabolismJ Nutr.(2003 Apr)
- ^Sehayek E, Nath C, Heinemann T, McGee M, Seidman CE, Samuel P, Breslow JLU-shape relationship between change in dietary cholesterol absorption and plasma lipoprotein responsiveness and evidence for extreme interindividual variation in dietary cholesterol absorption in humans.J Lipid Res.(1998-Dec)
- ^Nestel PJ, Poyser AChanges in cholesterol synthesis and excretion when cholesterol intake is increased.Metabolism.(1976-Dec)
- ^Jacobson TA, Maki KC, Orringer CE, Jones PH, Kris-Etherton P, Sikand G, La Forge R, Daniels SR, Wilson DP, Morris PB, Wild RA, Grundy SM, Daviglus M, Ferdinand KC, Vijayaraghavan K, Deedwania PC, Aberg JA, Liao KP, McKenney JM, Ross JL, Braun LT, Ito MK, Bays HE, Brown WV, Underberg JA,National Lipid Association Recommendations for Patient-Centered Management of Dyslipidemia: Part 2.J Clin Lipidol.(2015)







