What is iron?
Iron is one of the most abundant minerals on Earth. It occurs naturally in various foods such as oysters, legumes, chocolate, spinach, beef, and potatoes, and is added to some foods (e.g., cereals) as a fortification measure. Iron is also sold as a supplement in the form of capsules, tablets, or liquid. In hospital settings, it can be administered through intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) injection.[1]
Dietary iron comes in two primary forms: heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron is more readily absorbed; it is formed when iron binds to a heterocyclic organic compound called porphyrin. Heme iron is a component of hemoproteins like hemoglobin (Hb), an oxygen transport protein, and myoglobin, an oxygen-storage protein found in muscle tissues. Animal products (e.g., meat, poultry, and fish) contain both heme and non-heme iron, whereas plant-based and iron-fortified foods only provide non-heme iron, which is less easily absorbed by the body.[1]
Additionally, iron is a constituent of the iron-sulfur clusters (ISCs)[5] found in many proteins; iron is also present in proteins responsible for iron storage and transport (i.e., transferrin, lactoferrin, ferritin, hemosiderin).[6]
What are iron’s main benefits?
Iron plays a pivotal role in numerous biological functions and is often the first-line treatment for iron deficiency anemia (IDA). While specific guidelines exist for treating IDA with iron, there is still insufficient evidence to prove the benefits of iron supplementation in individuals with iron deficiency (ID) who are not anemic.[7]
In clinical practice, iron is commonly prescribed to menstruating women due to the increased blood loss, and during pregnancy to meet heightened metabolic demands and prevent IDA, which could have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby.[8][9]
ID is also a risk factor for heart failure (HF). Iron supplementation in individuals affected by HF appears to reduce the rates of hospitalization and the severity of HF symptoms.[10][11] Hemoglobin, ferritin and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) levels also seem to be increased by iron,[10] and one meta-analysis also noted that exercise capacity and quality of life were improved after iron supplementation in people with HF.[11]
Iron is also a key component in the brain, and studies involving children have shown that supplementation may improve memory and concentration.[12] However, more quality research is needed to verify these results.
The question of whether iron supplementation benefits infants and young adults remains a topic of debate necessitating further research. One meta-analysis, which included children and adolescents ranging from 1 month to 19 years old, found that iron supplementation increased Hb and ferritin levels, particularly with frequent supplementation over longer periods, and resulted in reduced prevalence of overall anemia, ID, and IDA.[13]
Finally, one meta-analysis demonstrated that both oral and IV iron supplementation appeared to improve symptoms of restless leg syndrome (RLS). Specifically, IV supplementation with ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) was associated with a significant improvement in quality of life (QOL) scores, although it had no noticeable effect on sleep quality.[14]
What are iron’s main drawbacks?
Iron supplements should be used cautiously, only when required, and in accordance with recommended doses. Prolonged use of iron supplements or an excess of iron in the system can lead to adverse side effects.
Iron supplements frequently result in gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms such as nausea, abdominal pain, dark stool, heartburn, and constipation, and other side effects such as headache. This can be a significant challenge for individuals with IDA, who may find it difficult to adhere to their treatment recommendations.[12]
Although ferritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin play essential roles in regulating iron levels in the system, an excessive amount of free iron can trigger the production of free radicals and increase oxidative stress. This can potentially lead to damage to proteins and cells, and harm the body.[15][16] Diseases characterized by iron overload include hemochromatosis, a hereditary disease in which iron builds up to toxic levels in the body, which can lead to damage to organs such as liver, joints pancreas or heart.[17]
Additionally, multiple observational studies have reported that regular consumption of dietary iron, especially heme iron sourced from meat products, may predispose one to numerous diseases (e.g., type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease) and may increase the risk of some cancers (e.g., breast, colorectal, and esophageal cancer). However, the majority of these claims are based on self-reported food diaries or food questionnaires, and the level of evidence is weak. Furthermore, it’s important to highlight that processed meat does not only contain heme iron, but other potentially harmful substances (e.g., nitrite, nitrate, heterocyclic amines) which may be confounding factors that also raise the risk of some diseases.[17]
In children, low doses of iron may cause diarrhea, but they do not appear to increase the risk of infections at the recommended dosage. Nevertheless, the World Health Organization (WHO) advises monitoring children in countries at high risk of malaria when receiving iron supplementation, as it may both increase the risk of contracting the disease and potentially worsen its effects. The mechanism by which iron interacts with malaria is still not fully understood.[12][18]
How does iron work?
Understanding the process of iron absorption in the body is key to grasping its mechanism of action. The disparity in absorption between heme and non-heme iron has implications for the amount of elemental iron absorbed in the body, with heme iron, typically found in animal products, being absorbed more efficiently.[19]
Both heme and non-heme iron are primarily absorbed in the duodenum and, to a lesser extent, in the upper jejunum (the first and second sections of the small intestine, respectively). Heme iron enters the gastrointestinal tract as ferrous iron (i.e., with a 2+ oxidation state), which is more easily absorbed, while non-heme iron is typically ingested in its ferric (3+) form. However, for non-heme iron to be absorbed, it must first be reduced into ferrous iron by reductase enzymes (e.g., ascorbate ferrireductase), or other compounds like vitamin C. Ferrous iron is then taken up by enterocytes lining the intestine through the divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), and then leaves these cells and enters the bloodstream via ferroportin. Once in the bloodstream, iron is converted back from ferrous to ferric iron and transported by transferrin to various organs and tissues.[20]
After absorption, iron plays a crucial role in several reactions and biological processes within the body, many of which are centered around iron’s roles in protein function and oxygen transport and storage. Iron is required to form hemoglobin (an oxygen-transporter protein) and myoglobin (an oxygen-storage protein). Inadequate iron intake can hinder the production of healthy red blood cells, potentially leading to anemia. In mitochondria, iron serves as a cofactor in proteins that contain iron-sulfur clusters (e.g., flavoproteins), other heme-containing proteins involved in the electron transport chain (e.g., cytochrome c oxidase), and proteins that contain iron ions (e.g., monooxygenases and dioxygenases).[21][10] Additionally, iron is involved in cell growth and differentiation, electron transfer reactions for energy production, and the regulation of the expression of some genes.[15]
Iron is also an essential nutrient for brain development and function. It plays a role in energy (ATP) production and neurotransmitter synthesis, as well as in the uptake and degradation of neurotransmitters, all of which are involved in behavior, memory, learning, and sensory systems.[12][22]
It’s important to note that when iron supplements are taken to treat IDA, it usually takes about 3 months to replenish iron stores, and hemoglobin levels will increase gradually in the first month of supplementation.[23]
What are other names for Iron
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Ferrous Fumarate
- Ferrous Gluconate
- Ferrous Bisglycinate
- Elemental Iron
- Heme Iron Polypeptide
Dosage information
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) depends on gender, age, and whether you are pregnant or lactating:[1][2]
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 months | 0.27 mg* | 0.27 mg* | ||
| 7–12 months | 11 mg | 11 mg | ||
| 1–3 years | 7 mg | 7 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 10 mg | 10 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 8 mg | 8 mg | ||
| 14–18 years | 11 mg | 15 mg | 27 mg | 10 mg |
| 19–50 years | 8 mg | 18 mg | 27 mg | 9 mg |
| 51+ years | 8 mg | 8 mg |
These values correspond to the RDA for total iron, which encompasses both dietary iron (iron assimilated from iron-rich foods) and iron supplements. The need for supplementation depends on the amount of iron absorbed from one's diet. It’s important to avoid exceeding the RDA to prevent excessive iron intake.[1]
Notably, for infants up to 6 months of age, these values specifically refer to adequate intake (AI), because there is insufficient evidence to establish an RDA for this age group.[1] The Institute of Medicine (IOM) determined the daily AI by multiplying the average iron content in human milk (0.35 mg/L) by the average milk intake of exclusively breastfed infants (0.78 L/day), resulting in an AI of 0.27 mg/day of iron. These values don’t account for potential variations in the iron concentration of human milk.[3]
For preterm breastfed infants, a daily oral iron dosage of approximately 2 mg/kg is estimated to be appropriate for preventing iron deficiency (ID) or iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in preterm breastfed babies. Term breastfed infants typically do not require additional iron until around 4 months, at which point supplementation with 1 mg/kg of iron may or may not be required depending on the infant's health status. Formula-fed preterm and term infants may require different dosages if iron supplementation is needed.[2]
It is worth noting that iron is most effective when administered on an empty stomach or 2 hours after a meal. However, if iron supplements are poorly tolerated due to gastrointestinal side effects, a dose reduction or administration after a meal may be more suitable.[4]
Examine Database: Iron
Research FeedRead all studies
In this randomized controlled trial, supplementation with iron during menstruation did not affect the amount of menstrual bleeding or hemoglobin levels in women without anemia.
Frequently asked questions
Iron is one of the most abundant minerals on Earth. It occurs naturally in various foods such as oysters, legumes, chocolate, spinach, beef, and potatoes, and is added to some foods (e.g., cereals) as a fortification measure. Iron is also sold as a supplement in the form of capsules, tablets, or liquid. In hospital settings, it can be administered through intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IM) injection.[1]
Dietary iron comes in two primary forms: heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron is more readily absorbed; it is formed when iron binds to a heterocyclic organic compound called porphyrin. Heme iron is a component of hemoproteins like hemoglobin (Hb), an oxygen transport protein, and myoglobin, an oxygen-storage protein found in muscle tissues. Animal products (e.g., meat, poultry, and fish) contain both heme and non-heme iron, whereas plant-based and iron-fortified foods only provide non-heme iron, which is less easily absorbed by the body.[1]
Additionally, iron is a constituent of the iron-sulfur clusters (ISCs)[5] found in many proteins; iron is also present in proteins responsible for iron storage and transport (i.e., transferrin, lactoferrin, ferritin, hemosiderin).[6]
Iron plays a pivotal role in numerous biological functions and is often the first-line treatment for iron deficiency anemia (IDA). While specific guidelines exist for treating IDA with iron, there is still insufficient evidence to prove the benefits of iron supplementation in individuals with iron deficiency (ID) who are not anemic.[7]
In clinical practice, iron is commonly prescribed to menstruating women due to the increased blood loss, and during pregnancy to meet heightened metabolic demands and prevent IDA, which could have serious consequences for both the mother and the baby.[8][9]
ID is also a risk factor for heart failure (HF). Iron supplementation in individuals affected by HF appears to reduce the rates of hospitalization and the severity of HF symptoms.[10][11] Hemoglobin, ferritin and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) levels also seem to be increased by iron,[10] and one meta-analysis also noted that exercise capacity and quality of life were improved after iron supplementation in people with HF.[11]
Iron is also a key component in the brain, and studies involving children have shown that supplementation may improve memory and concentration.[12] However, more quality research is needed to verify these results.
The question of whether iron supplementation benefits infants and young adults remains a topic of debate necessitating further research. One meta-analysis, which included children and adolescents ranging from 1 month to 19 years old, found that iron supplementation increased Hb and ferritin levels, particularly with frequent supplementation over longer periods, and resulted in reduced prevalence of overall anemia, ID, and IDA.[13]
Finally, one meta-analysis demonstrated that both oral and IV iron supplementation appeared to improve symptoms of restless leg syndrome (RLS). Specifically, IV supplementation with ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) was associated with a significant improvement in quality of life (QOL) scores, although it had no noticeable effect on sleep quality.[14]
Although iron is typically prescribed during pregnancy to prevent IDA,[8][9] regardless of the mother’s iron levels, more studies should be conducted to verify its benefits throughout pregnancy and after childbirth.
One meta-analysis has assessed the effect of daily iron supplementation in pregnant iron-replete women and found that it may reduce both maternal IDA and maternal ID at term (i.e., at 37 weeks gestation or later). The results also suggested that daily oral iron supplementation may decrease the risk of newborns being small for gestational age (SGA) (i.e., having a birth weight below the 10th percentile for their gestational age) or low birthweight (LBW) (i.e., having a birth weight lower than 2500 g).[9] Another meta-analysis, which included pregnant and non-pregnant women of reproductive age with IDA, found a significant increase in hemoglobin and ferritin levels following iron supplementation.[8] However, both meta-analyses presented high heterogeneity, risk of bias, and low to moderate levels of evidence, leaving some questions about the benefits and safety of preventative iron supplementation unanswered.
Oral iron replacement therapy is typically the first-line treatment for IDA. Iron is available in different forms (e.g., tablets, liquid) and compounds (e.g., ferrous sulfate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous bisglycinate, etc.), each of which provides different amounts of elemental iron.[23]
Here are some of the most common forms of iron found in supplements:
| Iron salt form | Elemental iron (%) | Elemental iron (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous sulfate | 20 | 64 |
| Ferrous fumarate | 33 | 99 |
| Ferrous gluconate | 12 | 39 |
Formulations containing ferrous iron (Fe2+) are more bioavailable, but they are also more likely to cause side effects. In contrast, ferric iron (Fe3+) preparations are usually better-tolerated but not as effective.[4]
Ferrous bisglycinate is another popular iron form found in supplements, wherein iron is chelated to two glycine molecules. Ferrous bisglycinate is marketed as more bioavailable than the other iron salts, and as having fewer gastrointestinal side effects. Furthermore, due to its stable chemical structure, ferrous bisglycinate is less affected by common iron absorption inhibitors (e.g., phytates found in cereals). However, although results from a meta-analysis showed that while iron bisglycinate was more effective than other iron salts in increasing hemoglobin levels in pregnant women, in children its effectiveness was comparable to other iron preparations.[24]
Heme iron polypeptide (HIP) is another form of iron. It is commonly produced from swine or bovine blood using enzymatic hydrolysis, in which heme iron is bound to peptides derived from the digested hemoglobin.[25] This form of iron has increased in popularity due to claims that it has enhanced bioavailability and fewer gastrointestinal side effects than other iron compounds. One study showed that when compared to ferrous fumarate, HIP taken with meals significantly increased iron absorption, but was not associated with side effects.[26] However, larger studies should be conducted to compare its efficacy and safety to other iron preparations.
When iron is administered intravenously, IV ferric carboxymaltose and IV iron sucrose appear to be the most effective forms at increasing hemoglobin and ferritin levels within a period of four weeks.[27]
Finally, one in vitro study compared modified-release iron supplements to immediate-release formulations and found that the slow-release tablets did not completely dissolve even after 24 hours, and iron uptake was considerably lower compared to regular tablets.[28] Although modified-release iron preparations may be better tolerated, with fewer side effects, they may not be as effective. These findings need further clarification through in vivo clinical studies.
It remains unclear whether iron supplementation is beneficial for athletes with ID but not anemia, or for those with normal iron status. While there is some evidence that iron supplementation may improve fatigue in iron-deficient athletes and non-athletes,[7] and intensive training is a potential cause of iron depletion,[52] only a few studies have investigated the benefits of iron supplementation in athletes with adequate iron levels to replenish iron loss due to training.
In one study involving iron-sufficient soccer players during training, iron supplementation was found to maintain ferritin and iron store levels, and these levels decreased once the supplementation was interrupted.[53] However, this study did not observe any significant difference in transferrin levels, which provide information on the iron levels required for erythropoiesis (red blood cell production), and it lacked a control group.
In another study, swimmers between the ages of 12 and 17 were either given an iron supplement (47 mg iron daily) or instructed to consume an iron-rich diet. Both interventions failed to significantly alter either the participants’ iron status (measured as iron, ferritin, and transferrin levels) or their athletic performance.[54]
While most people obtain adequate iron from their diet, there are situations where iron supplementation may be required.[1] For instance, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends daily oral iron supplementation for all children living in areas where anemia prevalence exceeds 40%.
Frequent blood donation can also deplete iron levels, potentially leading to anemia, and therefore supplementation may be necessary, especially for people at high risk of deficiency, such as women.[58][59] However, evidence that iron supplementation is effective in preserving iron levels is still weak.
Finally, individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to increase their iron intake,[1] mainly because plant-based foods contain non-heme iron, which is not as bioavailable as the heme iron found in meat.
Iron supplements should be used cautiously, only when required, and in accordance with recommended doses. Prolonged use of iron supplements or an excess of iron in the system can lead to adverse side effects.
Iron supplements frequently result in gastrointestinal discomfort, including symptoms such as nausea, abdominal pain, dark stool, heartburn, and constipation, and other side effects such as headache. This can be a significant challenge for individuals with IDA, who may find it difficult to adhere to their treatment recommendations.[12]
Although ferritin, hemosiderin, and transferrin play essential roles in regulating iron levels in the system, an excessive amount of free iron can trigger the production of free radicals and increase oxidative stress. This can potentially lead to damage to proteins and cells, and harm the body.[15][16] Diseases characterized by iron overload include hemochromatosis, a hereditary disease in which iron builds up to toxic levels in the body, which can lead to damage to organs such as liver, joints pancreas or heart.[17]
Additionally, multiple observational studies have reported that regular consumption of dietary iron, especially heme iron sourced from meat products, may predispose one to numerous diseases (e.g., type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease) and may increase the risk of some cancers (e.g., breast, colorectal, and esophageal cancer). However, the majority of these claims are based on self-reported food diaries or food questionnaires, and the level of evidence is weak. Furthermore, it’s important to highlight that processed meat does not only contain heme iron, but other potentially harmful substances (e.g., nitrite, nitrate, heterocyclic amines) which may be confounding factors that also raise the risk of some diseases.[17]
In children, low doses of iron may cause diarrhea, but they do not appear to increase the risk of infections at the recommended dosage. Nevertheless, the World Health Organization (WHO) advises monitoring children in countries at high risk of malaria when receiving iron supplementation, as it may both increase the risk of contracting the disease and potentially worsen its effects. The mechanism by which iron interacts with malaria is still not fully understood.[12][18]
Understanding the process of iron absorption in the body is key to grasping its mechanism of action. The disparity in absorption between heme and non-heme iron has implications for the amount of elemental iron absorbed in the body, with heme iron, typically found in animal products, being absorbed more efficiently.[19]
Both heme and non-heme iron are primarily absorbed in the duodenum and, to a lesser extent, in the upper jejunum (the first and second sections of the small intestine, respectively). Heme iron enters the gastrointestinal tract as ferrous iron (i.e., with a 2+ oxidation state), which is more easily absorbed, while non-heme iron is typically ingested in its ferric (3+) form. However, for non-heme iron to be absorbed, it must first be reduced into ferrous iron by reductase enzymes (e.g., ascorbate ferrireductase), or other compounds like vitamin C. Ferrous iron is then taken up by enterocytes lining the intestine through the divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), and then leaves these cells and enters the bloodstream via ferroportin. Once in the bloodstream, iron is converted back from ferrous to ferric iron and transported by transferrin to various organs and tissues.[20]
After absorption, iron plays a crucial role in several reactions and biological processes within the body, many of which are centered around iron’s roles in protein function and oxygen transport and storage. Iron is required to form hemoglobin (an oxygen-transporter protein) and myoglobin (an oxygen-storage protein). Inadequate iron intake can hinder the production of healthy red blood cells, potentially leading to anemia. In mitochondria, iron serves as a cofactor in proteins that contain iron-sulfur clusters (e.g., flavoproteins), other heme-containing proteins involved in the electron transport chain (e.g., cytochrome c oxidase), and proteins that contain iron ions (e.g., monooxygenases and dioxygenases).[21][10] Additionally, iron is involved in cell growth and differentiation, electron transfer reactions for energy production, and the regulation of the expression of some genes.[15]
Iron is also an essential nutrient for brain development and function. It plays a role in energy (ATP) production and neurotransmitter synthesis, as well as in the uptake and degradation of neurotransmitters, all of which are involved in behavior, memory, learning, and sensory systems.[12][22]
It’s important to note that when iron supplements are taken to treat IDA, it usually takes about 3 months to replenish iron stores, and hemoglobin levels will increase gradually in the first month of supplementation.[23]
Heme iron is more readily absorbed compared to non-heme iron, but the bioavailability of iron in the body can be influenced by several foods and dietary components. In individuals following a mixed diet, which includes fruit, vegetables, meat, and seafood, the bioavailability of iron ranges from approximately 14% to 18%. For vegetarian diets, iron bioavailability can range from 5% to 12%.[1]
Animal protein appears to increase non-heme iron absorption from non-meat produce (e.g., vegetables, grains) when these foods are consumed in the same meal. However, this effect was less pronounced for wheat than for other plant-based foods.[29][30] Additionally, studies have yielded mixed results regarding the combination of pork meat with meals high in phytates (which can be found in certain legumes and vegetables), indicating that phytate may counteract the positive effects of animal protein on non-heme iron absorption.[31][32]
It’s often recommended that iron be taken with Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) supplements or vitamin C-rich foods. Theoretically, ascorbic acid can facilitate the reduction of ferric iron to its more bioavailable form (ferrous iron), and can chelate iron ions (i.e., bond with them) to enhance their solubility and absorption from the intestines into the bloodstream.[33] Furthermore, ascorbate (a mineral salt of ascorbic acid) regulates the uptake of iron by transferrin, which is why scurvy (a disease resulting from a vitamin C deficiency) is often associated with some degree of iron-deficiency anemia.[34] However, two meta-analyses both found no difference in hemoglobin and ferritin levels when iron was supplemented with vitamin C, compared to iron alone,[33][35] suggesting that there is still limited clinical data on the benefits of combining iron and vitamin C.
Iron absorption can be reduced by other vitamins and minerals found both in supplements and foods.
Multiple studies have found that calcium is a strong inhibitor of iron absorption, and avoiding the simultaneous use of calcium and iron supplements may be beneficial. In one study, calcium phosphate inhibited iron absorption from a ferrous sulfate supplement, whether taken with or without food. In contrast, calcium carbonate only inhibited iron absorption when both supplements were consumed with food, suggesting that if a combined iron and calcium carbonate supplement is required, it should be taken between meals.[36] Calcium citrate, on the other hand, reduced iron absorption both with and without food, but not to a statistically significant degree in one study[36], and reduced absorption of non-heme iron without food in another study.[37]. The impact of calcium chloride on iron absorption seems to vary depending on whether it’s taken with food[38] or without food.[39]
Furthermore, a wide variety of beverages with a high antioxidant content, including coffee and tea, have some acute inhibitory effects on non-heme iron absorption. Coffee may reduce iron absorption,[40] possibly due to the presence of chlorogenic acid, a known iron chelator.[41] This mechanism can be extended to green coffee extract, which is an even richer source of chlorogenic acid. Tea, whether green[42] or black,[40] might inhibit iron absorption, possibly due to the presence of catechins[42] and theaflavins.[43] Infusions of chamomile, lime flower, pennyroyal, peppermint, and vervain may also reduce non-heme iron absorption.[40]
Rosemary (a source of rosmarinic acid), rich in phytic and phenolic acid, has also been shown to reduce non-heme iron absorption.[42]
Additionally, in one randomized controlled trial, people with beta-thalassemia who took 500 mg of quercetin (a chelator of iron[44]) per day for 12 weeks alleviated iron overload (a common complication of beta-thalassemia), notably reducing serum iron, ferritin, and inflammatory markers.[45]
Lastly, although zinc has the potential to reduce the absorption of iron, the effect is inconsistent, and the strength of this effect is unclear, with different studies reporting varying results.[13][46][47][48][49] The interaction between zinc and iron seems to be linked to competition for transporters in the liver, such as divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), human copper transporter 1 (hCTR1),[50] and ZRT/IRT-like protein 14 (Zip14).[51] Taking zinc between meals is likely a good way to prevent any interference with iron absorption.
It’s important to note that the typical Western diet is complex and rich in both iron absorption enhancers and inhibitors, whose effects may both be attenuated when these substances are consumed simultaneously.[1]
Iron supplementation is often associated with gastrointestinal side effects, which may impact treatment adherence. As a result, researchers have explored different dosages and frequencies of supplementation.
One meta-analysis looked at intermittent (once, twice, or three times per week) iron supplementation vs. daily supplementation for improving iron status and preventing anemia in menstruating adolescent and adult women. Both had similar effects on hemoglobin levels and the risk of anemia. However, daily supplementation proved more effective in increasing ferritin levels (although with low quality of evidence), which may be especially significant in populations with a high prevalence of ID, which is characterized by adequate levels of hemoglobin but low ferritin and/or transferrin saturation.[55] Moreover, there were no significant differences in treatment adherence or in the side effects experienced among participants in the two groups.[18] There is currently no evidence that intermittent supplementation offers advantages in terms of fewer side effects or improved adherence compared to daily supplementation.
In another study, iron-depleted (but not deficient) participants took the same iron dose either daily or on alternate days for 14 and 28 days, respectively. The alternate-day dosing regimen resulted in reduced levels of hepcidin (a hormone responsible for regulating iron homeostasis in the body) and greater iron absorption. However, the impact on iron status remained unclear because there were no notable differences in serum iron, ferritin, or hemoglobin levels between the two groups at the end of the trial. Additionally, the alternate-day dosing group reported experiencing less nausea but more headaches.[56] A subsequent study by the same author, including individuals with ID, confirmed these findings. However, the study’s duration was too short to assess the long-term effects on iron status.[57]
Cast iron pans are popular, especially for searing, and are generally safe to use. But they can leach iron, which is a strong pro-oxidant. Those genetically at risk for iron overload should learn more about cast iron safety.
For well over a thousand years, cast iron has been used as a reliable cooking surface. Actually, it's been used since the appropriately named “Iron Age,” roughly 2500 years ago.
Fast forward a couple millennia, and we’ve been thrust into the “Spend all day on the Internet Age”. People are starting to question the healthiness of everything, including the venerable cast iron. And not without reason: just because cast iron’s been used for years, by many people who lived long and healthy lives, doesn’t necessarily mean it’s the healthiest option for your frying pan.
Let’s explore this issue in depth. What exactly is cast iron? Are there any plausible mechanisms by which it might harm health? What does the research say?
Paying the iron price
Cast iron is relatively easy to analyze, as far as health effects go. It’s made out of … iron. Not like the more complex pans, which have multiple layers or man-made coatings. So let’s start by talking a little bit about iron.
You can’t just dig up pure iron from the ground. Pure iron is rare and mainly comes from fallen meteorites. And it's actually pretty soft, so not great for making pans without adding in some carbon for hardening. But still, around 97-98% of a cast iron pan is plain ol’ iron, which is why we’re so interested in its health effects. Our discussion also applies to carbon steel cookware (such as woks), which is made up of 99% iron.
Other than being such an important material for making pans and skyscrapers, iron is also an essential dietary mineral. And cooking on a cast iron pan can transfer some of that mineral from the pan to the food to your body. Some will see this as a good thing, especially considering that 1.6 billion people around the world are anemic, with iron deficiency being the main cause.[60] But iron-deficiency anemia in the US is much less common, with 5 million people having iron-deficiency anemia.[61]
So when most people think of iron, they think of getting enough iron. Iron is one of the few nutrients that a doctor will ask you about, and iron even takes up one of the coveted nutrient spots on the US nutrition label! But the same property that makes iron so useful in the body, its ability to give or receive electrons, makes it potentially harmful when you ingest too much, due to increased production of free radicals.[62][63]
Too much iron has been linked to a wide variety of conditions, such as Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and colorectal cancer to name just a few.[64][65][66] There’s a couple groups of people who don’t have to worry quite as much about iron overload though: menstruating women and vegetarians/vegans. But for others, especially those who regularly eat red meat, it doesn’t take much to push yourself into excess iron territory.
Chances of iron overload in different people
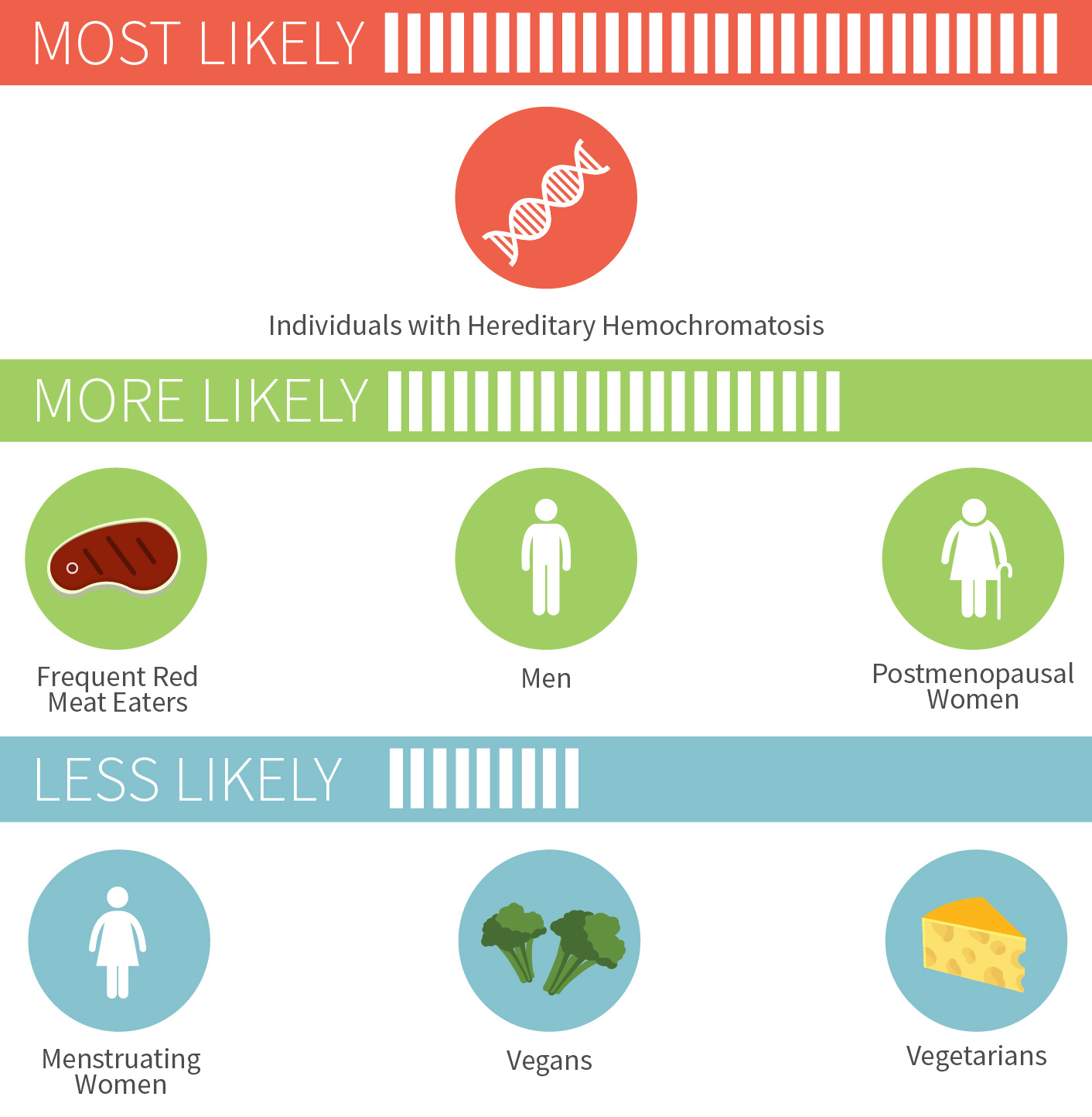
For the nearly one million Americans who have hereditary hemochromatosis, a condition that typically emerges in adulthood where you absorb too much dietary iron, the risk is much more serious. As is the risk of iron poisoning in children, which started being recognized in the 1980s and led to removal of iron from some children’s multivitamins.[67][68]
Certain multivitamins and foods (especially breakfast cereals) have iron added to them, which can contribute to iron buildup over time in those that don’t get rid of iron once a month, namely all males and all non-menstruating females. One of the most popular multivitamins on pharmacy shelves has 100% of the iron RDA per pill, and that one extremely popular breakfast cereal (the one with the bee who’s always up in your business for some reason) contains almost 50% of the iron RDA. A bowl or two of cereal a day, plus red meat a few times a week, a few iron-fortified energy bars, a multivitamin… the iron can add up really quickly.
There are three general strategies for limiting iron. The first is to simply eat less of it, like by switching to an iron-free multivitamin (if you choose to take one at all). Second, you can take advantage of the various iron-absorption inhibitors, such as coffee and certain plant phytochemicals.[69] The third method seems like the most radical option: donate blood every once in awhile, and ditch some of the iron trapped in your red blood cells.[70]
Note that while regular blood donation helps both you and others, and is quite effective at normalizing iron levels according to a randomized trial,[71] it's not always well tolerated.[72] Other than reducing iron in the diet, certain supplements may be able to reduce iron levels, and curcumin has shown efficacy specifically for iron overload.[73]
How much iron are we talking?
We’re talking a pretty decent amount of iron, depending on the condition of your cast iron pan, and what specifically you’re cooking.
To put it into context: men need 8 mg of iron a day, and a serving of tomato sauce cooked in a cast iron skillet can provide 5 mg of iron![74]
Iron content of foods cooked in a cast iron pan

This effect is so reliable that iron cookware has occasionally been used to combat anemia. A variety of studies have shown that iron pots and pans can boost your iron status, substantially increasing the iron content of certain foods (like eggs and applesauce) but not others (like hamburgers).[75][76] The pan’s iron is in the non-heme form, which isn’t absorbed as well as heme iron from meat. But vitamin C can greatly increase absorption, as can acidity, so recipes containing things like lemon or tomato sauce can boost absorption.
If you don’t want your cast iron pan to leach so much iron, make sure it’s well seasoned. Since acidic foods help transfer iron from the pan into your food, you want to put a barrier between the acid and the iron. And that barrier is seasoning, which we’ll talk about in the next section. A pan that is newer and more likely to stick food will also leach more iron than an ancient and heavily seasoned pan. Three other factors that cause more leaching are: using liquid, increased cooking time, and mixing the food more often.
Some of you may be wondering why cast iron (and carbon steel) are uniquely susceptible to this leaching process. What about stainless steel? Steel is made out of iron, after all.
Well, the key to the anti-stain property of stainless pans is chromium, which makes up about 10% or more of the pan. A thin layer of chromium oxide makes stainless steel pans moisture and rust resistant, unlike cast iron pans which can rust very easily. While moisture finds it hard to get INTO the stainless steel pan, a side-benefit is that iron finds it hard to get OUT of the pan. So iron leaching isn’t a big concern here.
That doesn’t mean stainless steel is 100% safe for everyone. While iron overload is a risk that applies to many millions of people, a far smaller number of people are allergic to nickel and chromium, and both of these metals can theoretically leach from stainless steel pans.[77][78] For people with severe nickel or other metal allergies, an enameled pan may be a safe bet.
Cast iron seasoning … aka oxidizing oil on purpose
Aside from iron, there are two other possible dangers of using cast iron pans. One is that you could drop a heavy pan onto your foot or hurt your wrist maneuvering it around. This is only partially a joke, as some cast iron pans can get EXTREMELY heavy compared to all other types of pans. The other possible danger is only theoretical at this point: the risk from eating tiny bits of flaked-off seasoning from the pan’s surface.
So what exactly is seasoning? Well, cast iron pans can easily collect moisture and develop rust. To prevent that, and also get a nice non-stick finish, you have to season the pan with oil rich in polyunsaturated fats. Ideally, you’d continue to season it over the course of years, with more usage adding to the seasoning layers. Like wine and cheese, cast iron is one of the few things that get better with time.
The chemistry is pretty simple. First, get a largely unsaturated fat, like flaxseed oil. For the same reason you don’t want to overload your body with a ton of polyunsaturated fats, that they’re easily oxidized, these fats can be useful on cast iron. When exposed to high heat on top of iron, which acts as a catalyst, the unsaturated fatty acids oxidize, then polymerize into a coating that fills in pores. Further heating carbonizes/hardens the coating.
A well-seasoned pan will appear deep black, and will be almost non-stick. Pans that are pre-seasoned in the factory are not actually well-seasoned; they’re just seasoned enough to prevent rust. You have to keep adding thin layers of fat over time to get that perfect seasoning, since attempting to add one thick layer all at once will result in a greasy pan, with largish pieces chunking off. And it takes a certain heat range to form a good seasoning layer. Really high heats (like above 500° F) will burn off all the seasoning, while low heats (like less than 300° F) won’t encourage enough polymerization of the fatty acids.
The pros of the seasoning process are numerous: you can eventually cook eggs without them sticking, you don’t have to re-season as often, the pan won’t rust, and you can get much cooking cred from your foodie friends.
The cons are harder to quantify. Bits of the seasoning will come off over time (and be replaced by more seasoning). Nobody knows exactly how much comes off over time, nor do they know what the health effects are of eating tiny bits of this type of broken down fat. If you heat the pan up fairly high over long periods, might carcinogenic fumes or free radicals develop from the oxidized oil?[79] Would small amounts of these hypothetical byproducts even be of concern, given the natural antioxidant defenses our bodies employ?
Despite this uncertainty, you shouldn’t be overly alarmed. The flaxseed oil seasoning on your cast iron pan may be oxidized, but it’s not rancid — meaning, it doesn’t impart undesirable odors or flavors (for the most part). This may seem confusing at first, since all the double bonds in a bottle of flaxseed oil mean that it can go rancid easily when not refrigerated. This is because the double bonds are easily attacked by air and light, among other factors.
But when you season your pan using flaxseed oil and heat, the double bonds don’t get randomly attacked. Rather, the double bonds in the flaxseed oil open up and form bonds with neighboring flaxseed fatty acids, with the help of iron and air. It’s a delicate game — gently heating a pot of flaxseed oil would be a recipe for rancidity, but doing it in a thin layer with the help of a really hot iron pan and air… that creates the oh-so-useful seasoning.
Given the lack of certainty about health effects, it’s easy to get alarmed. But if you want to get really up in arms about seasoning, you’d better make sure to also stay away from other heated foods that contain known carcinogens, like the acrylamide in browned potatoes and in breakfast cereals, heterocyclic amines in cooked meat, etc etc.[80][81][82] Remember that toxicity lies in the dose. You don’t have to boil or steam all your foods in order to live a long and healthy life.
I hate science, just tell me if I should ditch my cast iron
If cast iron has been used for so many centuries, and hasn’t shown obvious harm, why even question it at all? There are at least two good reasons.
First, many other types of pans are available, and it’s a buyer’s market. Cast iron is actually not an optimal material for many types of cooking (which we’ll get into in a second), so you definitely don’t need to own a cast iron pan.
Second, and most important, people often cook with their pan on a near-daily basis. Over the years, that adds up to a lot of exposure to whatever the pan gives off.
Cast iron is great for a lot of reasons. It’s cheap, it can and will last a lifetime and get better with age, and you can safely throw it into a super hot oven. All that heavy iron also means that these pans retain heat really well, so they excel in tasks like searing a thick and juicy steak. Some other, thinner pans wouldn’t do as well, since a cold steak would drop down the pan’s temperature upon contact. Another benefit is that the fairly-nonstick nature of cast iron pans will still allow it to develop a “fond” (which is French for “base” or “foundation”) on the bottom, if you happen to enjoy making delicious fond-based sauces.
On the con side, cast iron is extremely heavy and not that easy to take care of (at least until it’s older and well-seasoned). Carbon steel pans are similar in function, but around 25% lighter. Plus they’re a bit smoother, which makes them slightly more non-stick than cast iron, unless you sand down your cast iron pan like some cooking fanatics do. But cast iron isn’t actually a very good heat conductor, so it’s prone to developing hot-spots and cold-spots. Not good if you want even cooking. And since carbon steel is thinner, it’s even more prone to uneven heating.
Another con has to do with our old enemy (or friend if you’re anemic), leached iron. If you make a tomato sauce using a cast iron pan, and it tastes weird, there’s a chance the leached iron is the culprit. Again, seasoned pans are your friend, both for non-stick purposes and for avoiding off-tastes in cooked food.
These cons can be mitigated by using more than one type of pan. Different pans are good at different things, so having more than one pan around might be a good idea if you’re into cooking. Even the much-hated Teflon pan is often used by discerning chefs to make eggs. It doesn’t leach anything under normal heat conditions, and even ingesting tiny amounts of Teflon shouldn’t really harm you, since it’s inert. Heating a Teflon pan under high heat for long periods though … those toxic fumes aren’t great for your health and especially your bird’s health.[83][84]
Even with all the options available, there is no perfect pan, given the wide variety of factors people look at. These include non-stickiness, searing ability, ease of use, even heating, and so on and so on. Cast iron does well with some of these and poorly with others.
We might never know the exact health effects of cast iron pans. Eating bits of oxidized oil every day might seem unwise, but a perhaps more likely detriment is getting too much iron, especially when using a newer or less-seasoned pan.
The decision to choose cast iron or a different cooking material depends on a variety of personal preferences, including risk aversion, what you enjoy cooking with, and what you already own. Trying out more than one type of pan may be wise, or even using more than one type of pan on a regular basis, depending on what’s best suited for the job at hand.
Update History
Full page update
Written By
Edited By
Reviewed By
References
- ^Iron Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. MedlinePlus. National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS). Updated 2023 Jun 15; cited 2023 December 5
- ^Baker RD, Greer FR,Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0-3 years of age).Pediatrics.(2010-Nov)
- ^Baker et al.Diagnosis and Prevention of Iron Deficiency and Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young Children (0–3 Years of Age)Pediatrics.(2010-11-01)
- ^Aksu T, Ünal ŞIron Deficiency Anemia in Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence.Turk Arch Pediatr.(2023-Jul)
- ^Bandyopadhyay S, Chandramouli K, Johnson MKIron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis.Biochem Soc Trans.(2008-Dec)
- ^Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on MicronutrientsDietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Chapter 9, Iron(2001)
- ^Houston BL, Hurrie D, Graham J, Perija B, Rimmer E, Rabbani R, Bernstein CN, Turgeon AF, Fergusson DA, Houston DS, Abou-Setta AM, Zarychanski REfficacy of iron supplementation on fatigue and physical capacity in non-anaemic iron-deficient adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trialsBMJ Open.(2018 Apr 5)
- ^Ali SA, Razzaq S, Aziz S, Allana A, Ali AA, Naeem S, Khowaja N, Ur Rehman FRole of iron in the reduction of anemia among women of reproductive age in low-middle income countries: insights from systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health.(2023-Apr-17)
- ^Hansen R, Sejer EPF, Holm C, Schroll JBIron supplements in pregnant women with normal iron status: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand.(2023-Sep)
- ^Hamed M, Elseidy SA, Ahmed A, Thakker R, Mansoor H, Khalili H, Mohsen A, Mamas MA, Banerjee S, Kumbhani DJ, Elgendy IY, Elbadawi AIntravenous iron therapy among patients with heart failure and iron deficiency: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Heliyon.(2023-Jun)
- ^Hamza M, Sattar Y, Manasrah N, Patel NN, Rashdi A, Khanal R, Naveed H, Zafar M, Khan AM, Alharbi A, Aamir M, Gonuguntla K, Raina S, Balla SMeta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Iron in Patients With Iron Deficiency and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction.Am J Cardiol.(2023-Sep-01)
- ^Gutema BT, Sorrie MB, Megersa ND, Yesera GE, Yeshitila YG, Pauwels NS, De Henauw S, Abbeddou SEffects of iron supplementation on cognitive development in school-age children: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One.(2023)
- ^Andersen CT, Marsden DM, Duggan CP, Liu E, Mozaffarian D, Fawzi WWOral iron supplementation and anaemia in children according to schedule, duration, dose and cosupplementation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 129 randomised trials.BMJ Glob Health.(2023-Feb)
- ^Tomer Avni, Shelley Reich, Nirit Lev, Anat Gafter-GviliIron supplementation for restless legs syndrome - A systematic review and meta-analysisEur J Intern Med.(2019 May)
- ^Deli C. K., et alIron Supplementation and Physical PerformanceCurrent Issues in Sports and Exercise Medicine.(2013 May)
- ^Brissot P, Ropert M, Le Lan C, Loréal ONon-transferrin bound iron: a key role in iron overload and iron toxicityBiochim Biophys Acta.(2012 Mar)
- ^Charlebois E, Pantopoulos KNutritional Aspects of Iron in Health and Disease.Nutrients.(2023-May-24)
- ^Fernández-Gaxiola AC, De-Regil LMIntermittent iron supplementation for reducing anaemia and its associated impairments in adolescent and adult menstruating womenCochrane Database Syst Rev.(2019 Jan 31)
- ^Carpenter CE, Mahoney AWContributions of heme and nonheme iron to human nutritionCrit Rev Food Sci Nutr.(1992)
- ^Sharp P, Srai SKMolecular mechanisms involved in intestinal iron absorptionWorld J Gastroenterol.(2007 Sep 21)
- ^Paul BT, Manz DH, Torti FM, Torti SVMitochondria and Iron: current questions.Expert Rev Hematol.(2017-Jan)
- ^Chen Z, Yang H, Wang D, Sudfeld CR, Zhao A, Xin Y, Chen JC, Fawzi WW, Xing Y, Li ZEffect of Oral Iron Supplementation on Cognitive Function among Children and Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients.(2022-Dec-15)
- ^Arulparithi CS, Arunbabu T, Manjani SIron Preparations in the Management of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Indian Pediatr.(2023-Sep-15)
- ^Fischer JAJ, Cherian AM, Bone JN, Karakochuk CDThe effects of oral ferrous bisglycinate supplementation on hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev.(2023-Jul-10)
- ^Tansukkasem S, Kaewpathomsri P, Jonjaroen V, Payongsri P, Lertsiri S, Niamsiri NProduction and Characterization of Heme Iron Polypeptide from the Blood of Skipjack Tuna () Using Enzymatic Hydrolysis for Food Supplement Application.Foods.(2023-Aug-29)
- ^Seligman et al.Clinical studies of hip: An oral heme-iron productNutrition Research.(2000-09-01)
- ^Rogozińska E, Daru J, Nicolaides M, Amezcua-Prieto C, Robinson S, Wang R, Godolphin PJ, Saborido CM, Zamora J, Khan KS, Thangaratinam SIron preparations for women of reproductive age with iron deficiency anaemia in pregnancy (FRIDA): a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet Haematol.(2021-Jul)
- ^Zariwala MG, Somavarapu S, Farnaud S, Renshaw DComparison study of oral iron preparations using a human intestinal model.Sci Pharm.(2013)
- ^Lynch SR, Hurrell RF, Dassenko SA, Cook JDThe effect of dietary proteins on iron bioavailability in manAdv Exp Med Biol.(1989)
- ^Reddy MB, Hurrell RF, Cook JDMeat consumption in a varied diet marginally influences nonheme iron absorption in normal individualsJ Nutr.(2006 Mar)
- ^Bach Kristensen M, Hels O, Morberg C, Marving J, Bügel S, Tetens IPork meat increases iron absorption from a 5-day fully controlled diet when compared to a vegetarian diet with similar vitamin C and phytic acid contentBr J Nutr.(2005 Jul)
- ^Baech SB, Hansen M, Bukhave K, Jensen M, Sørensen SS, Kristensen L, Purslow PP, Skibsted LH, Sandström BNonheme-iron absorption from a phytate-rich meal is increased by the addition of small amounts of pork meatAm J Clin Nutr.(2003 Jan)
- ^Loganathan V, Bharathi A, Prince AM, Ramakrishnan JTreatment efficacy of vitamin C or ascorbate given as co-intervention with iron for anemia - A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental studies.Clin Nutr ESPEN.(2023-Oct)
- ^Lane DJ, Richardson DRThe active role of vitamin C in mammalian iron metabolism: much more than just enhanced iron absorption!Free Radic Biol Med.(2014-Oct)
- ^Duarte AFM, Carneiro ACSV, Peixoto ATBMM, Montenegro DFP, Campos DSC, Alves APR, Costa ARMM, Fino APMOral Iron Supplementation in Pregnancy: Current Recommendations and Evidence-Based Medicine.Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet.(2021-Oct)
- ^Cook JD, Dassenko SA, Whittaker PCalcium supplementation: effect on iron absorptionAm J Clin Nutr.(1991 Jan)
- ^Candia V, Ríos-Castillo I, Carrera-Gil F, Vizcarra B, Olivares M, Chaniotakis S, Pizarro FEffect of various calcium salts on non-heme iron bioavailability in fasted women of childbearing ageJ Trace Elem Med Biol.(2018 Sep)
- ^Hallberg L, Brune M, Erlandsson M, Sandberg AS, Rossander-Hultén LCalcium: effect of different amounts on nonheme- and heme-iron absorption in humansAm J Clin Nutr.(1991 Jan)
- ^Gaitán D, Flores S, Saavedra P, Miranda C, Olivares M, Arredondo M, López de Romaña D, Lönnerdal B, Pizarro FCalcium does not inhibit the absorption of 5 milligrams of nonheme or heme iron at doses less than 800 milligrams in nonpregnant womenJ Nutr.(2011 Sep)
- ^R F Hurrell, M Reddy, J D CookInhibition of non-haem iron absorption in man by polyphenolic-containing beveragesBr J Nutr.(1999 Apr)
- ^Kono Y, Kashine S, Yoneyama T, Sakamoto Y, Matsui Y, Shibata HIron chelation by chlorogenic acid as a natural antioxidant.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.(1998-Jan)
- ^Samman S, Sandström B, Toft MB, Bukhave K, Jensen M, Sørensen SS, Hansen MGreen tea or rosemary extract added to foods reduces nonheme-iron absorption.Am J Clin Nutr.(2001-Mar)
- ^O'Coinceanainn M, Bonnely S, Baderschneider B, Hynes MJReaction of iron(III) with theaflavin: complexation and oxidative products.J Inorg Biochem.(2004-Apr)
- ^Leopoldini M, Russo N, Chiodo S, Toscano MIron chelation by the powerful antioxidant flavonoid quercetinJ Agric Food Chem.(2006 Aug 23)
- ^Sajadi Hezaveh Z, Azarkeivan A, Janani L, Hosseini S, Shidfar FThe effect of quercetin on iron overload and inflammation in β-thalassemia major patients: A double-blind randomized clinical trialComplement Ther Med.(2019 Oct)
- ^Olivares M, Pizarro F, Ruz M, de Romaña DLAcute inhibition of iron bioavailability by zinc: studies in humansBiometals.(2012 Aug)
- ^O'Brien KO, Zavaleta N, Caulfield LE, Yang DX, Abrams SAInfluence of prenatal iron and zinc supplements on supplemental iron absorption, red blood cell iron incorporation, and iron status in pregnant Peruvian womenAm J Clin Nutr.(1999 Mar)
- ^Nguyen P, Grajeda R, Melgar P, Marcinkevage J, Flores R, Ramakrishnan U, Martorell REffect of zinc on efficacy of iron supplementation in improving iron and zinc status in womenJ Nutr Metab.(2012)
- ^de Brito NJ, Rocha ÉD, de Araújo Silva A, Costa JB, França MC, das Graças Almeida M, Brandão-Neto JOral zinc supplementation decreases the serum iron concentration in healthy schoolchildren: a pilot studyNutrients.(2014 Sep 4)
- ^Espinoza A, Le Blanc S, Olivares M, Pizarro F, Ruz M, Arredondo MIron, copper, and zinc transport: inhibition of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) and human copper transporter 1 (hCTR1) by shRNABiol Trace Elem Res.(2012 May)
- ^Liuzzi JP, Aydemir F, Nam H, Knutson MD, Cousins RJZip14 (Slc39a14) mediates non-transferrin-bound iron uptake into cellsProc Natl Acad Sci U S A.(2006 Sep 12)
- ^Wouthuyzen-Bakker M, van Assen SExercise-induced anaemia: a forgotten cause of iron deficiency anaemia in young adults.Br J Gen Pract.(2015-May)
- ^Escanero JF, Villanueva J, Rojo A, Herrera A, del Diego C, Guerra MIron stores in professional athletes throughout the sports season.Physiol Behav.(1997-Oct)
- ^Tsalis G, Nikolaidis MG, Mougios VEffects of iron intake through food or supplement on iron status and performance of healthy adolescent swimmers during a training season.Int J Sports Med.(2004-May)
- ^Al-Nassem, A. et alIron deficiency without anemia: a diagnosis that mattersClin Med.
- ^Stoffel NU, Cercamondi CI, Brittenham G, Zeder C, Geurts-Moespot AJ, Swinkels DW, Moretti D, Zimmermann MBIron absorption from oral iron supplements given on consecutive versus alternate days and as single morning doses versus twice-daily split dosing in iron-depleted women: two open-label, randomised controlled trialsLancet Haematol.(2017 Nov)
- ^Stoffel NU, Zeder C, Brittenham GM, Moretti D, Zimmermann MBIron absorption from supplements is greater with alternate day than with consecutive day dosing in iron-deficient anemic womenHaematologica.(2019 Aug 14)
- ^Milman N, Kirchhoff MInfluence of blood donation on iron stores assessed by serum ferritin and haemoglobin in a population survey of 1433 Danish males.Eur J Haematol.(1991-Aug)
- ^Garry PJ, VanderJagt DJ, Wayne SJ, Koehler KH, Rhyne RL, Simon TLA prospective study of blood donations in healthy elderly personsTransfusion.(1991 Oct)
- ^McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, Wojdyla D, de Benoist BWorldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005Public Health Nutr.(2009 Apr)
- ^Clark SFIron deficiency anemiaNutr Clin Pract.(2008 Apr-May)
- ^Emerit J, Beaumont C, Trivin FIron metabolism, free radicals, and oxidative injuryBiomed Pharmacother.(2001 Jul)
- ^McCord JMIron, free radicals, and oxidative injurySemin Hematol.(1998 Jan)
- ^Kell DBTowards a unifying, systems biology understanding of large-scale cellular death and destruction caused by poorly liganded iron: Parkinson's, Huntington's, Alzheimer's, prions, bactericides, chemical toxicology and others as examplesArch Toxicol.(2010 Nov)
- ^Fang X, An P, Wang H, Wang X, Shen X, Li X, Min J, Liu S, Wang FDietary intake of heme iron and risk of cardiovascular disease: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studiesNutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.(2015 Jan)
- ^Qiao L, Feng YIntakes of heme iron and zinc and colorectal cancer incidence: a meta-analysis of prospective studiesCancer Causes Control.(2013 Jun)
- ^Morris CCPediatric iron poisonings in the United StatesSouth Med J.(2000 Apr)
- ^Dean BS, Krenzelok EPMultiple vitamins and vitamins with iron: accidental poisoning in childrenVet Hum Toxicol.(1988 Feb)
- ^Brune M, Rossander L, Hallberg LIron absorption and phenolic compounds: importance of different phenolic structuresEur J Clin Nutr.(1989 Aug)
- ^Skikne B, Lynch S, Borek D, Cook JIron and blood donationClin Haematol.(1984 Feb)
- ^Sim Y Ong, Lyle C Gurrin, Lara Dolling, Jeanette Dixon, Amanda J Nicoll, Michelle Wolthuizen, Erica M Wood, Gregory J Anderson, Grant A Ramm, Katrina J Allen, John K Olynyk, Darrell Crawford, Louise E Ramm, Paul Gow, Simon Durrant, Lawrie W Powell, Martin B DelatyckiReduction of Body Iron in HFE-related Haemochromatosis and Moderate Iron Overload (Mi-Iron): A Multicentre, Participant-Blinded, Randomised Controlled TrialLancet Haematol.(2017 Dec)
- ^Fabrice Lainé, Marc Ruivard, Véronique Loustaud-Ratti, Fabrice Bonnet, Paul Calès, Edouard Bardou-Jacquet, Sylvie Sacher-Huvelin, Xavier Causse, Christine Beusnel, Alain Renault, Eric Bellissant, Yves Deugnier, Study GroupMetabolic and Hepatic Effects of Bloodletting in Dysmetabolic Iron Overload Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study in 274 PatientsHepatology.(2017 Feb)
- ^Elahe Mohammadi, Ahmad Tamaddoni, Durdi Qujeq, Esmat Nasseri, Farid Zayeri, Hamid Zand, Mahdi Gholami, Seyed Mostafa MirAn Investigation of the Effects of Curcumin on Iron Overload, Hepcidin Level, and Liver Function in β-Thalassemia Major Patients: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Clinical TrialPhytother Res.(2018 Sep)
- ^Brittin HC, Nossaman CEIron content of food cooked in iron utensilsJ Am Diet Assoc.(1986 Jul)
- ^Geerligs PD, Brabin BJ, Omari AAFood prepared in iron cooking pots as an intervention for reducing iron deficiency anaemia in developing countries: a systematic reviewJ Hum Nutr Diet.(2003 Aug)
- ^Adish AA, Esrey SA, Gyorkos TW, Jean-Baptiste J, Rojhani AEffect of consumption of food cooked in iron pots on iron status and growth of young children: a randomised trialLancet.(1999 Feb 27)
- ^Thyssen JP, Menné TMetal allergy--a review on exposures, penetration, genetics, prevalence, and clinical implicationsChem Res Toxicol.(2010 Feb 15)
- ^Kuligowski J, Halperin KMStainless steel cookware as a significant source of nickel, chromium, and ironArch Environ Contam Toxicol.(1992 Aug)
- ^Chiang TA, Wu PF, Ko YCIdentification of carcinogens in cooking oil fumesEnviron Res.(1999 Jul)
- ^Skog K, Viklund G, Olsson K, Sjöholm IAcrylamide in home-prepared roasted potatoesMol Nutr Food Res.(2008 Mar)
- ^Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K, Nakagama H, Nagao MHeterocyclic amines: Mutagens/carcinogens produced during cooking of meat and fishCancer Sci.(2004 Apr)
- ^Konings EJ, Ashby P, Hamlet CG, Thompson GAAcrylamide in cereal and cereal products: a review on progress in level reductionFood Addit Contam.(2007)
- ^Woodhall S, Stamford MPTFE toxicity in birdsVet Rec.(2004 Dec 11)
- ^Hamaya R, Ono Y, Chida Y, Inokuchi R, Kikuchi K, Tameda T, Tase C, Shinohara KPolytetrafluoroethylene fume-induced pulmonary edema: a case report and review of the literatureJ Med Case Rep.(2015 May 14)
Examine Database References
- Depression Symptoms - McClung JP, Karl JP, Cable SJ, Williams KW, Nindl BC, Young AJ, Lieberman HRRandomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of iron supplementation in female soldiers during military training: effects on iron status, physical performance, and moodAm J Clin Nutr.(2009 Jul)
- Aerobic Exercise Metrics - Waldvogel S, Pedrazzini B, Vaucher P, Bize R, Cornuz J, Tissot JD, Favrat BClinical evaluation of iron treatment efficiency among non-anemic but iron-deficient female blood donors: a randomized controlled trialBMC Med.(2012 Jan 24)
- Fatigue (non-anemic) - Favrat B, Balck K, Breymann C, Hedenus M, Keller T, Mezzacasa A, Gasche CEvaluation of a single dose of ferric carboxymaltose in fatigued, iron-deficient women--PREFER a randomized, placebo-controlled studyPLoS One.(2014 Apr 21)
- Hemoglobin - Ali SA, Razzaq S, Aziz S, Allana A, Ali AA, Naeem S, Khowaja N, Ur Rehman FRole of iron in the reduction of anemia among women of reproductive age in low-middle income countries: insights from systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health.(2023-Apr-17)
- Hemoglobin - Andersen CT, Marsden DM, Duggan CP, Liu E, Mozaffarian D, Fawzi WWOral iron supplementation and anaemia in children according to schedule, duration, dose and cosupplementation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 129 randomised trials.BMJ Glob Health.(2023-Feb)
- Heart Rate - Brownlie T 4th, Utermohlen V, Hinton PS, Giordano C, Haas JDMarginal iron deficiency without anemia impairs aerobic adaptation among previously untrained womenAm J Clin Nutr.(2002 Apr)
- Muscular Endurance - Brutsaert TD, Hernandez-Cordero S, Rivera J, Viola T, Hughes G, Haas JDIron supplementation improves progressive fatigue resistance during dynamic knee extensor exercise in iron-depleted, nonanemic womenAm J Clin Nutr.(2003 Feb)
- Anxiety Symptoms - Vaucher P, Druais PL, Waldvogel S, Favrat BEffect of iron supplementation on fatigue in nonanemic menstruating women with low ferritin: a randomized controlled trialCMAJ.(2012 Aug 7)
- Fatigue (non-anemic) - Verdon F, Burnand B, Stubi CL, Bonard C, Graff M, Michaud A, Bischoff T, de Vevey M, Studer JP, Herzig L, Chapuis C, Tissot J, Pécoud A, Favrat BIron supplementation for unexplained fatigue in non-anaemic women: double blind randomised placebo controlled trialBMJ.(2003 May 24)
- Fatigue (non-anemic) - Krayenbuehl PA, Battegay E, Breymann C, Furrer J, Schulthess GIntravenous iron for the treatment of fatigue in nonanemic, premenopausal women with low serum ferritin concentrationBlood.(2011 Sep 22)
- Fatigue (non-anemic) - Houston BL, Hurrie D, Graham J, Perija B, Rimmer E, Rabbani R, Bernstein CN, Turgeon AF, Fergusson DA, Houston DS, Abou-Setta AM, Zarychanski REfficacy of iron supplementation on fatigue and physical capacity in non-anaemic iron-deficient adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trialsBMJ Open.(2018 Apr 5)
- Aerobic Exercise Metrics - Woods A, Garvican-Lewis LA, Saunders PU, Lovell G, Hughes D, Fazakerley R, Anderson B, Gore CJ, Thompson KGFour weeks of IV iron supplementation reduces perceived fatigue and mood disturbance in distance runnersPLoS One.(2014 Sep 23)
- Fibromyalgia Symptoms - Chad S Boomershine, Todd A Koch, David MorrisA Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of Ferric Carboxymaltose in Iron-Deficient Patients with FibromyalgiaRheumatol Ther.(2018 Jun)
- Hemoglobin - Silva Neto LGR, Santos Neto JED, Bueno NB, de Oliveira SL, Ataide TDREffects of iron supplementation versus dietary iron on the nutritional iron status: Systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.(2019)
- Hemoglobin - Fischer JAJ, Cherian AM, Bone JN, Karakochuk CDThe effects of oral ferrous bisglycinate supplementation on hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Nutr Rev.(2023-Jul-10)
- Hemoglobin - Fernández-Gaxiola AC, De-Regil LMIntermittent iron supplementation for reducing anaemia and its associated impairments in adolescent and adult menstruating womenCochrane Database Syst Rev.(2019 Jan 31)
- Infant Birth Weight - Hansen R, Sejer EPF, Holm C, Schroll JBIron supplements in pregnant women with normal iron status: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand.(2023-Sep)
- Restless Leg Syndrome Symptoms - Tomer Avni, Shelley Reich, Nirit Lev, Anat Gafter-GviliIron supplementation for restless legs syndrome - A systematic review and meta-analysisEur J Intern Med.(2019 May)
- Attention - Gutema BT, Sorrie MB, Megersa ND, Yesera GE, Yeshitila YG, Pauwels NS, De Henauw S, Abbeddou SEffects of iron supplementation on cognitive development in school-age children: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One.(2023)
- Attention - Chen Z, Yang H, Wang D, Sudfeld CR, Zhao A, Xin Y, Chen JC, Fawzi WW, Xing Y, Li ZEffect of Oral Iron Supplementation on Cognitive Function among Children and Adolescents in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients.(2022-Dec-15)
- All-Cause Mortality - Mei Z, Chen J, Luo S, Jin L, Liu Q, Chen YComparative efficacy of intravenous and oral iron supplements for the treatment of iron deficiency in patients with heart failure: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Pharmacol Res.(2022-Aug)
- All-Cause Mortality - Hamza M, Sattar Y, Manasrah N, Patel NN, Rashdi A, Khanal R, Naveed H, Zafar M, Khan AM, Alharbi A, Aamir M, Gonuguntla K, Raina S, Balla SMeta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Iron in Patients With Iron Deficiency and Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction.Am J Cardiol.(2023-Sep-01)
- Cardiovascular Mortality - Hamed M, Elseidy SA, Ahmed A, Thakker R, Mansoor H, Khalili H, Mohsen A, Mamas MA, Banerjee S, Kumbhani DJ, Elgendy IY, Elbadawi AIntravenous iron therapy among patients with heart failure and iron deficiency: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Heliyon.(2023-Jun)









